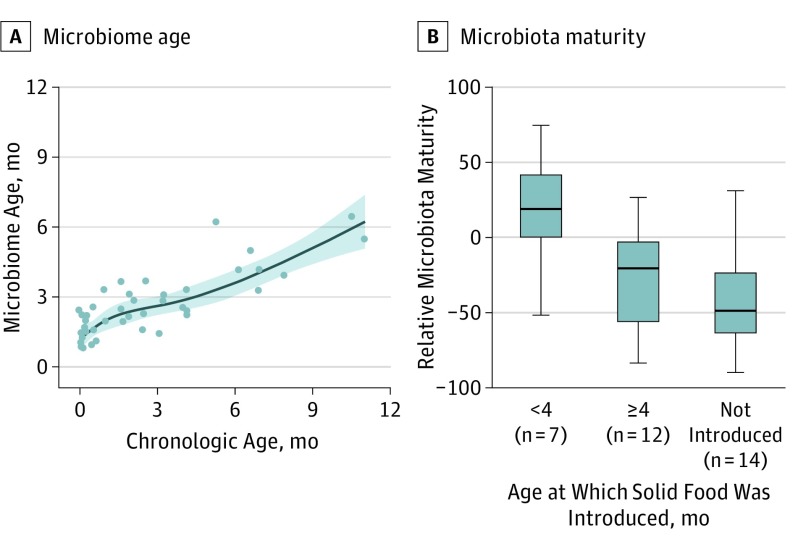
Figure 4. Microbiome Age Estimation.
A, A subset of healthy, vaginally born, exclusively breastfed infants (n = 42) was used to train a random forest regression model that was then applied to estimate microbiota maturity. Relative microbiota maturity was calculated by microbiota age of a child relative to the microbiota age of healthy children of the same chronologic age from the spline fit line shown here. B, Differences in relative microbiota maturity based on the age at which solid food was introduced in our cohort. Early solid food introduction was associated with early microbiota maturity (<4 months vs ≥4 months, P = .02; ≥4 months vs not introduced, P = .30, Kruskal-Wallis). Boxes indicate the 25th to 75th percentile; line within the box, median; error bars, 1.5 × interquartile range.