Figure 1.
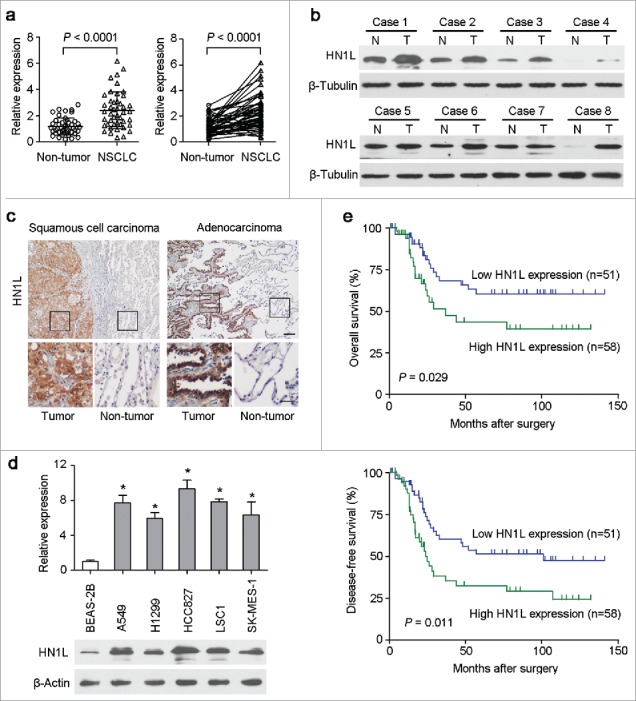
Overexpression of HN1L associated with poorer outcomes of NSCLCs. (a) Relative expression levels of HN1L detected by qPCR in 45 pairs of NSCLC tissues. (b) Western blot analysis of HN1L expression in matched primary tumor (T) samples and its corresponding non-tumor (N) tissues of 8 NSCLC cases. β-Tubulin was used as a loading control. (c) Representative IHC staining figures of HN1L expression in lung squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Scale bar, top figures, 100 μm; bottom figures, 50μm. (d) Relative expression levels of HN1L detected by qPCR and western blotting in an immortalized bronchial epithelial cell line (BEAS-2B) and other five NSCLC cell lines. Data represent mean ± SD. * P < 0.05. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (e) Kaplan-Meier analysis indicating the correlation of HN1L overexpression with poorer overall survival and disease-free survival rates of NSCLC patients.
