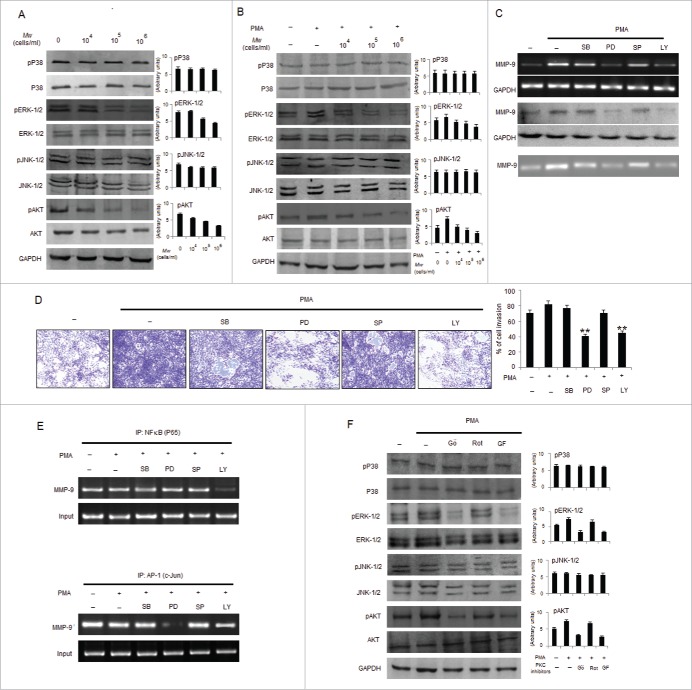
Figure 5.
Mw inhibits PMA-induced transcriptional activation of MMP-9 and phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and AKT in B16F10 cells. (A) 2×106 B16F10 cells were treated with Mw and the expression of phospho/total MAPKs and AKT were determined by protein gel blotting. (B) 2×106 B16F10 cells preincubated with Mw for 2hr followed by 80nM PMA for 24hr were subjected to western blot using antibodies specific to total/phospho MAPKs and AKT. Data are from one of 3 representative experiments with similar results. (C) Cells were treated with specific inhibitors of MAPKs or AKT for 1hr and then stimulated with PMA for 24hr. The MMP-9 mRNA (top), protein expression (middle) and activity (bottom) were analyzed by semi-quantitative RT-PCR, protein gel blot and gelatin zymography respectively. (D) Similarly cells were preincubated with specific inhibitors of MAPKs or AKT for 1hr and then stimulated with PMA for 24hr was seeded onto the upper chamber wells. After incubation for 24hr at 37°C, the filter was fixed and stained. The randomly chosen fields were photographed (20X). Data are shown as the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments. **P< 0.001 vs PMA alone treatment. (E) B16F10 cells treated with specific inhibitors of MAPKs or AKT for 1hr and then stimulated with PMA for 24hr were subjected to immunoprecipitation using NF-κB (IP: NF-κBP65) and AP-1 (IP: c-Jun) specific antibody. Semi quantitative RT-PCR amplify the putative NF-κB and AP1 binding sites at the MMP-9 promoter. Data are from one representative experiment performed at least thrice. (F) Cells were stimulated with 80nM PMA for 24hr after pretreatment with PKC inhibitors for 1hr, and the levels of total/phospho MAPKs and AKT were determined by western blotting. Data are from one of 3 representative experiments.