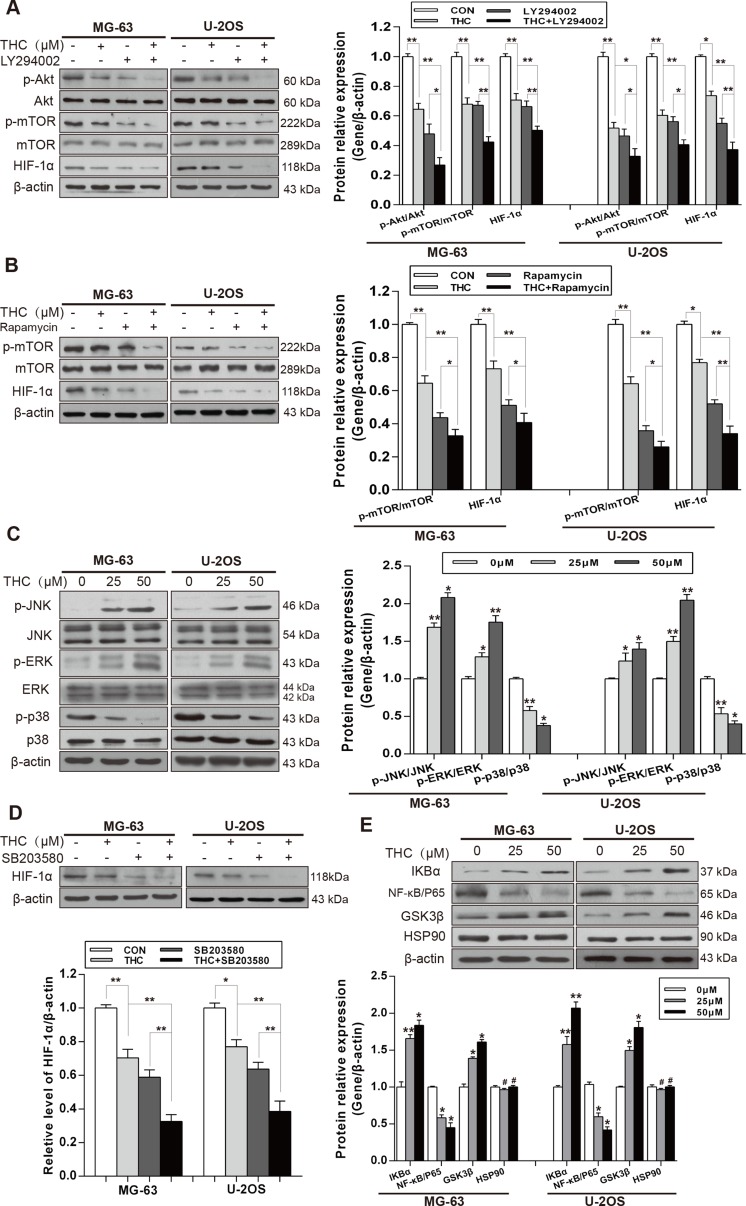
Figure 4. THC downregulates the expression of HIF-1α by suppressing Akt/mTOR and p38 MAPK signaling pathways.
(A) The expressions of Akt/mTOR pathway and HIF-1α in MG-63 and U-2OS cells were assessed by western blotting (Control, THC 25 μM, Akt inhibitor LY294002 20 μM and THC+LY294002 groups). (B) The expressions of mTOR and HIF-1α in MG-63 and U-2OS cells were assessed by western blotting (Control, THC 25 μM, mTOR inhibitor Rapamycin 20 nM, and THC+Rapamycin groups). (C) Western blotting to analyze the expression of p38 MAPK pathway in MG-63 and U-2OS cells treated with different concentrations of THC (0–50 μM). (D) The expressions of HIF-1α in MG-63 and U-2OS cells were assessed by western blotting (Control, THC 25 μM, p38 inhibitor SB203580 10 μM and THC+SB203580 groups). (E) Western blotting to analyze the expression of IKBα, NF-κB, GSK3β, and HSP90 in MG-63 and U-2OS cells treated with different concentrations of THC (0–50 μM). β-actin served as loading control. The bar graphs summarize the levels of proteins. All data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, #p > 0.05, not significant. THC, tetrahydrocurcumin; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; mTOR, mechanistic target of rapamycin; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; GSK3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3β; Hsp90, heat shock protein 90.