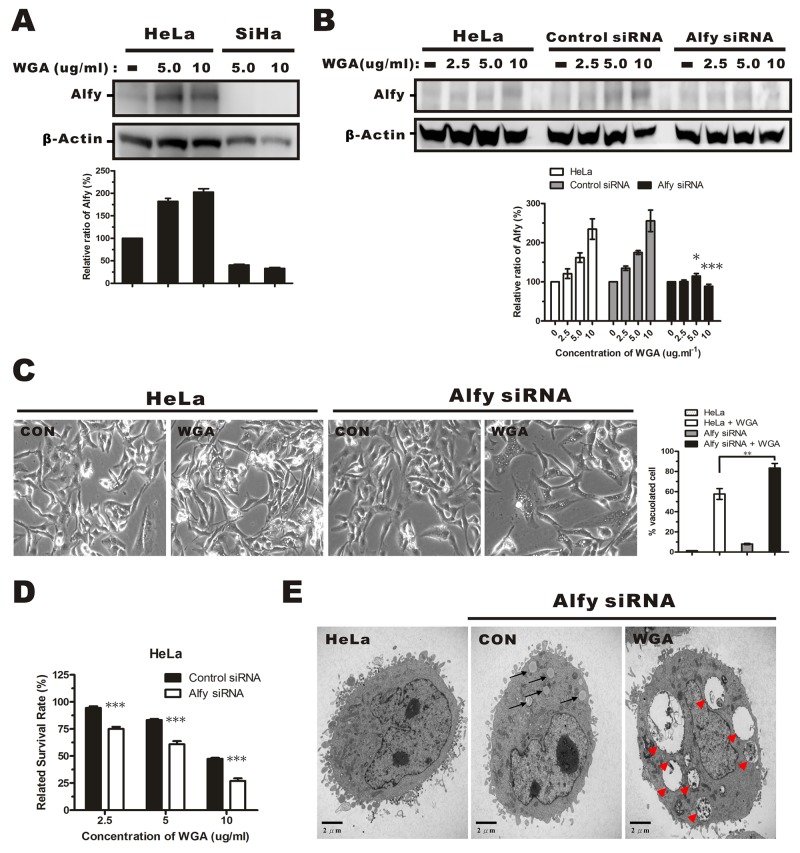
Figure 6. Effects of Alfy knockdown on WGA-induced cytoplasmic vacuolation and cell death.
(A) Western blotsof total cell lysates showing increased Alfy expression in HeLa cells, but not SiHa cells, after treatment with WGA (5.0 and 10 μg/mL) for 24 h. (B) Western blot showing Alfy expression in WGA-treated HeLa cells following knockdown of Alfy with shRNA. Empty vector (control siRNA) was used as negative control. The fold change in Alfy expression after WGA treatment was quantified using NIH ImageJ. The relative units were normalized to β-Actin and compared to untreated control cells. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD for three independent experiments. (*, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001) (C) Phase-contrast images showing the effects of Alfy knockdown on WGA-induced cytoplasmic vacuolation. Bar graph showing the percentage of vacuolated HeLa cells expressing control siRNA or Alfy siRNA with or without WGA treatment. At least 200 cells were counted in three independent experiments. Bars represent the mean ± SD (**, P < 0.01). (D) MTT assays of cell viability after treatment of Alfy knockdown and control HeLa cells with or without WGA for 24 h. Data represent an average of three independent experiments. Bars represent the mean ± SD (***, P < 0.001). (E) Formation of cytoplasmic vacuoles in HeLa cells following Alfy knockdown. Cells were transfected with Alfy siRNA and treated for 24 h with or without WGA (10 μg/mL). The black arrow head points to small vacuoles and the red arrow head points to extensive paraptosis-like vacuoles.