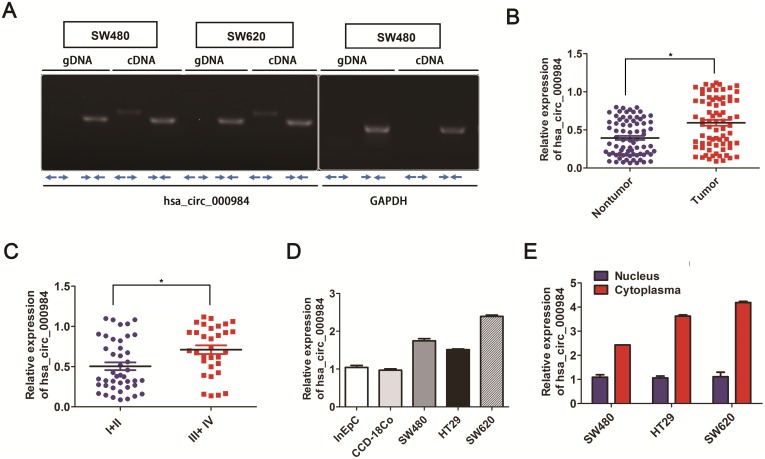
Figure 1. Analysis of hsa_circ_000984 expression in CRC.
(A) Hsa_circ_000984 could be significantly amplified in cDNA with divergent primers but did not amplify using genomic DNA as templates. Representative images of PCR products of hsa_circ_000984; GAPDH was used as a linear RNA control. (B) The results of hsa_circ_000984 expression level in CRC tissue samples and those matched colorectal nontumorous tissues were analyzed by qRT-PCR using divergent primer (**P<0.01, paired t-test). Data are shown as mean ± SD for three independent experiments (n=3). (C) The correlation analysis between hsa_circ_000984 expression level and TNM stage of CRC patients and hsa_circ_000984 expression was significantly associated with the advanced TNM stage (III+IV) (*P<0.05, logistic regression analysis). Data are shown as mean ± SD for three independent experiments (n=3). (D) qRT-PCR showed that hsa_circ_000984 was highly expressed in CRC cell lines of SW480, HT29 and SW620, compared with the normal colon-derived cell (CCD-18Co) and human intestinal epithelial cells (InEpC). (E) Levels of hsa_circ_000984 from nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of CRC cell lines analyzed by qRT-PCR showed that hsa_circ_000984 was mainly enriched in the cytoplasmic fraction. Error bars indicate SD. *P<0.05, two-side Student’s t-test.