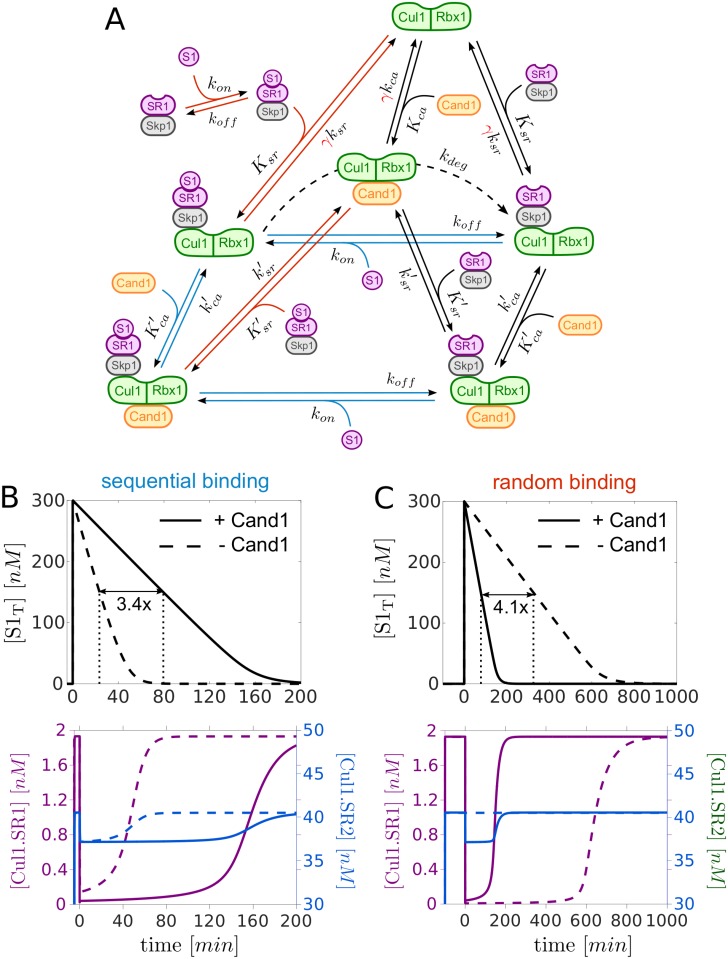
Fig 7. Alternative network architecture.
A: Extension of the Cand1 cycle model (black solid lines) to analyze different modes of substrate binding to SR1. Sequential mechanism: Substrate (S1) only binds to SR1 if the latter is already bound to Cul1 or Cul1.Cand1 (blue lines). Random order mechanism: S1 binds to free SR1, Cul1.SR1 and Cul1.Cand1.SR1. In addition, SR1.S1 binds to Cul1 or Cul1.Cand1 (red lines). By increasing the factor γ the binding affinity between Cul1 and SR1 can be lowered while still satisfying the detailed balance condition in Eq 1. For SR2 we used the scheme depicted in Fig 1B (without substrate), but with ksr and kca multiplied by γ. Ksr, Kca, and denote dissociation constants whereas ksr, kca, and are dissociation rate constants (cf. Table 1). B and C: Comparison of the half-life (t1/2) of S1 for two network designs: one with Cand1 (+Cand1) and tight binding of SRs to Cul1 (Cand1T = 390nM, γ = 1) and another one without Cand1 (-Cand1) and weak binding of SRs to Cul1 (Cand1T = 390nM, γ = 1.67 ⋅ 107). In the latter case γ is chosen such that the pre-stimulus steady state for Cul1.SR1 is the same in both cases (note that dashed and solid lines in lower panels partially overlap). If substrate binds sequentially the system without Cand1 (B, dashed line) outperforms the system with Cand1 (B, solid line) as the t1/2 is 3.4-fold larger in the presence of Cand1. In both cases Cul1 is redistributed from Cul1.SR2 to Cul1.SR1 and Cul1.SR1.S1 (B, lower panel). In contrast, when substrate binds in a random order (cf. panel A) its degradation is substantially delayed (4.1-fold) in the absence of Cand1 (C, dashed line) and redistribution of Cul1 only occurs in the presence of Cand1 (C, lower panel). Total substrate is defined as S1T = [S1] + [SR1.S1] + [Cul1.SR1.S1] + [Cul1.Cand1.SR1.S1]. Parameters: At t = 0 substrate S1 (300nM) was added to a steady state mixture containing Cul1T = 300nM, SR1T = 30nM and SR2T = 630nM. The values of Cand1T and γ are indicated in the upper panels. kon = 107M−1s−1, koff = 0.01s−1, kdeg = 0.004s−1. Parameters other than those mentioned are listed in Table 1.