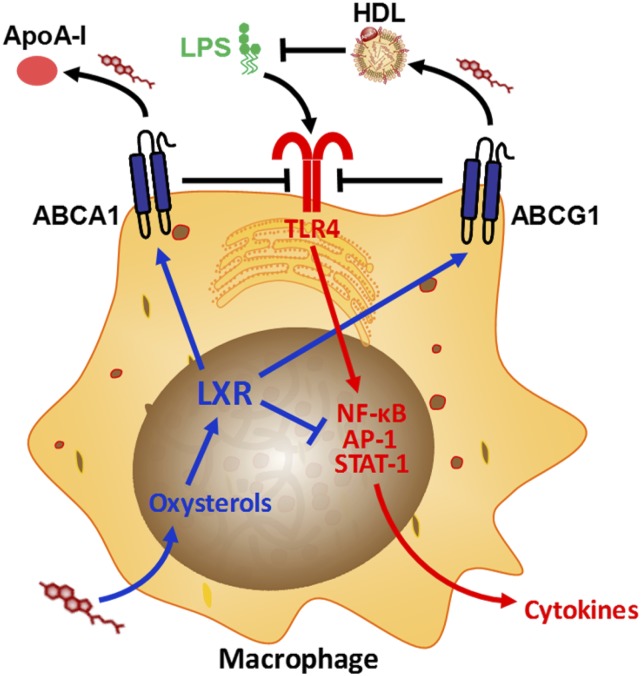
Figure 2.
Interactions between cholesterol and proinflammatory Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling in the macrophage. Oxysterols accumulate upon cholesterol internalization by the macrophage, activating liver X receptor (LXR). LXR up-regulates the cholesterol efflux proteins ATP-binding cassette A1 and G1 (ABCA1 and ABCG1, respectively) and inhibits proinflammatory cytokine induction by suppressing the activity of transcription factors (i.e., nuclear factor-κB [NF-κB], activator protein [AP]-1, and signal transducer and activator of transcription [STAT]-1) at gene promoters. ABCA1 and ABCG1 inhibit TLR4 activation in the plasma membrane through reducing lipid raft cholesterol (through promoting cholesterol efflux to the extracellular acceptors apolipoprotein A-I [ApoA-I] and high-density lipoprotein [HDL], respectively). HDL also directly suppresses lipopolysaccharide (LPS) signaling by binding and neutralizing LPS.