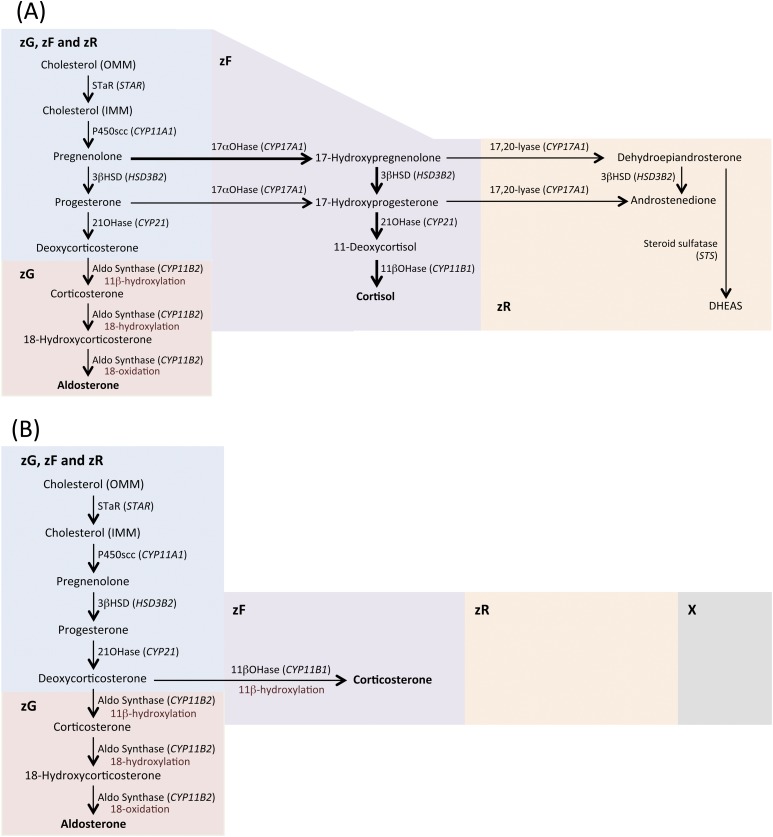
Figure 1.
Cholesterol is mobilized from a store in the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) and is transferred by steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) to the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM), where it is converted to pregnenolone by P450scc, the first and rate-limiting step of steroidogenesis (9, 10). Aldosterone biosynthesis is restricted to the zG, where aldosterone synthase is localized. (A) In humans, the activity of 17α-hydroxylase (17αOHase)/17,20 lyase (CYP17A1) is a key enzyme for the synthesis of both cortisol and androgens; the main biosynthetic pathway for cortisol synthesis is via the 17α-hydroxylation of pregnenolone, indicated by thicker arrows. (B) Mice, like other rodents, do not express CYP17A1 and, as a result, the major glucocorticoid synthesized is corticosterone (instead of cortisol), which is produced from deoxycorticosterone by 11β-hydroxylase [11βOHase (Cyp11b1)] in the zF. (A and B) The absence of CYP17A1 expression in mice means that adrenal androgens cannot be synthesized as in humans in the zR, and mice do not have a distinguishable zR. (B) Young mice have an X-zone that degenerates by the first pregnancy in females and by sexual maturity in males. Figure 1 includes data from Stowasser and Gordon (10). 21OHase, 21-hydroxylase; 3βHSD, 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase; Aldo synthase, aldosterone synthase; DHEAS, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate; STS, steroid sulfatase.