Figure 8.
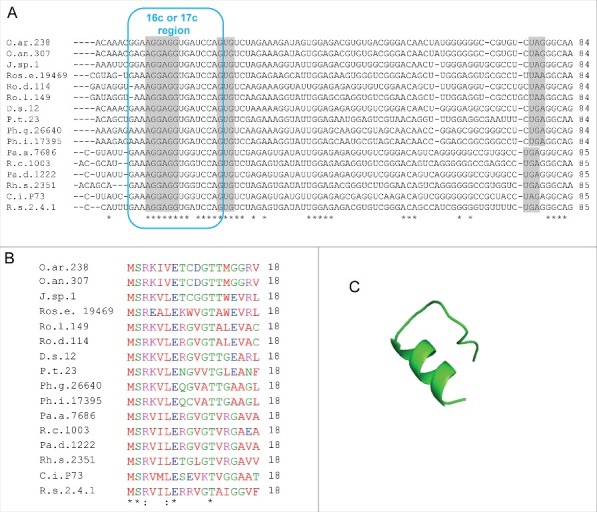
Putative rreB homologs in Rhodobacterales. (A) Multiple sequence alignment of sequences corresponding to the putative small mRNAs containing homologous sORFs of 18 codons (named rreR) and preceded by a region with extended complementarity to the 3′-end of 16 sRNA (Extended SD region). Canonical SD, GTG start codon and stop codons are highlighted in gray. For other descriptions see (Fig. 2A. (B) Multiple sequence alignment of the small proteins RreR encoded by the sORFs shown in A). O.ar.238, Octadecabacter arcticus 238; O.an.307, Octadecabacter antarcticus 307; J.sp.1, Jannaschia sp CCS 1; Ros.e.19469, Roseibacterium elongatum DSM 19469; Ro.d.114, Roseobacter denitrificans OCh 114; Ro.l.149, Roseobacter litoralis Och 149; D.s.12, Dinoroseobacter shibae DFL 12; P.t.23, Planktomarina temperata RCA 23; Ph.g.26640, Phaeobacter gallaeciensis DSM 26640; Ph.i.17395, Phaeobacter inhibens DSM 17395; Pa.a.7686, Paracoccus aminophilus JCM 7686; R.c.1003, Rhodobacter capsulatus SB 1003; Pa.d 1222, Paracoccus denitrificans PD 1222; Rh.s.2351, Rhodovulum sulfidophilum DSM 2351; C.i.P73, Celeribacter indicus strain P73; R.s.2.4.1., Rhodobacter spaheroides ATCC 2.4.1. (C) Predicted spatial structure of RreR from D. shibae DFL 12.
