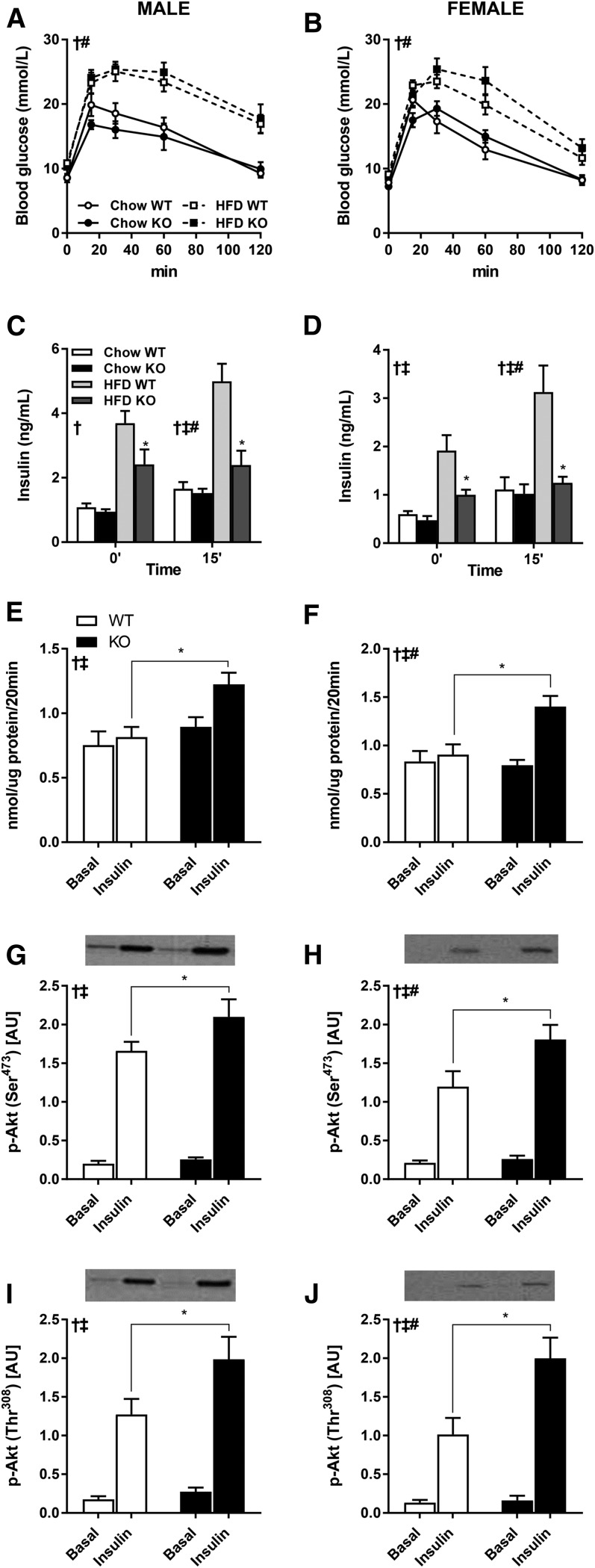
Fig. 4.
Glucose tolerance and skeletal muscle glucose uptake and signal transduction. Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance tests were performed in 4 h-fasted 15-week-old DGKζ KO and wild-type mice, after 10 weeks on HFD (n = 7–16). Plasma glucose (A, B) and insulin (C, D) concentration in male (A, C) and female (B, D) mice were assessed during the intraperitoneal glucose tolerance tests. EDL muscle was obtained from 17-week-old 4 h-fasted DGKζ KO and wild-type mice after 12 weeks on HFD and incubated ex vivo in the absence (basal) or presence of insulin (0.36 nmol/l) for measurement of glucose transport (E, F) and Akt Ser473 and Thr308 phosphorylation (G–J) in male (E, G, I) and female (F, H, J) mice (n = 9–13 mice). Two-way ANOVA or repeated measures two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post hoc testing. C, D: ‡P < 0.05 overall genotype difference, †P < 0.05 overall diet effect, #P < 0.05 interaction; *P < 0.05 versus wild-type mice on same diet. E–J: ‡P < 0.05 overall genotype difference, †P < 0.05 overall insulin effect, #P < 0.05 interaction; *P < 0.05 versus wild-type mice of same condition.