Fig. 9.
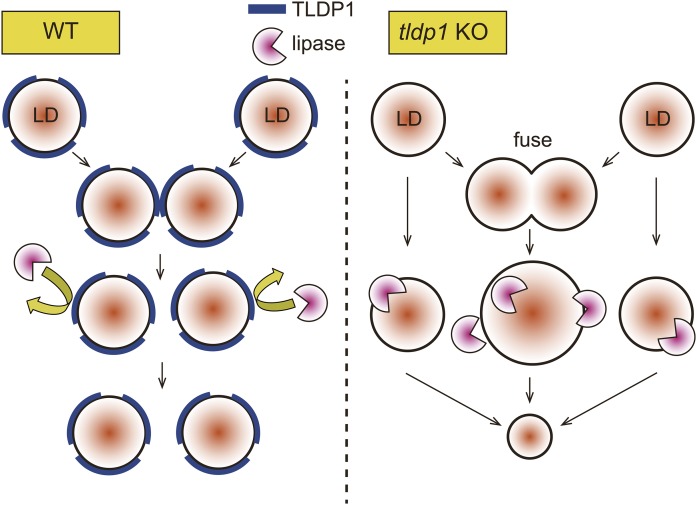
Possible functions of TLDP1 on LDs. We observed unusually large LDs in KO, but not in WT, and the number of LDs per cell markedly decreased in KO in comparison with WT (Fig. 6C), suggesting that unusually large LDs may have been generated by the fusion of several small LDs in KO (Fig. 6D). Furthermore, the ratio of DG/TG increased in KO in comparison with WT, suggesting the increase of lipolysis in KO (Fig. 8D). These abnormal phenotypes of KO were restored by expression of tldp1 in KO. These results suggest that TLDP1 protects LDs against lipase attack and inhibits the fusion of LDs (WT, left panel), while the deletion of TLDP1 accelerates the lipolysis and fusion of LDs (KO, right panel).