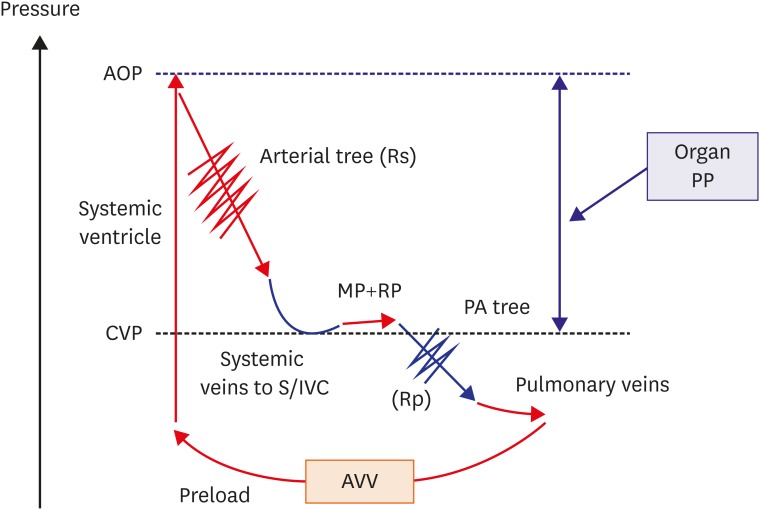
Figure 1.
Fontan hemodynamics without failure. In Fontan patients, the SV supports systemic circulation. High CVP is the driving pressure of the pulmonary circulation, and the MP and RP play significant roles in pulmonary circulation. Organ PP, or the pressure difference between CVP and AOP, is low due to high CVP and low systemic pressure from diminished cardiac preload. Rs (red jagged line) appropriately increases to maintain PP, while the Rp (blue jagged line) should remain low.
AOP = aortic pressure; AVV = atrioventricular valve; CVP = central venous pressure; MP = muscle pump; PA = pulmonary artery; PP = perfusion pressure; RP = respiratory pump; Rp = pulmonary artery resistance; Rs = systemic artery resistance; S/IVC = superior vena cava/inferior vena cava; SV = systemic ventricle.