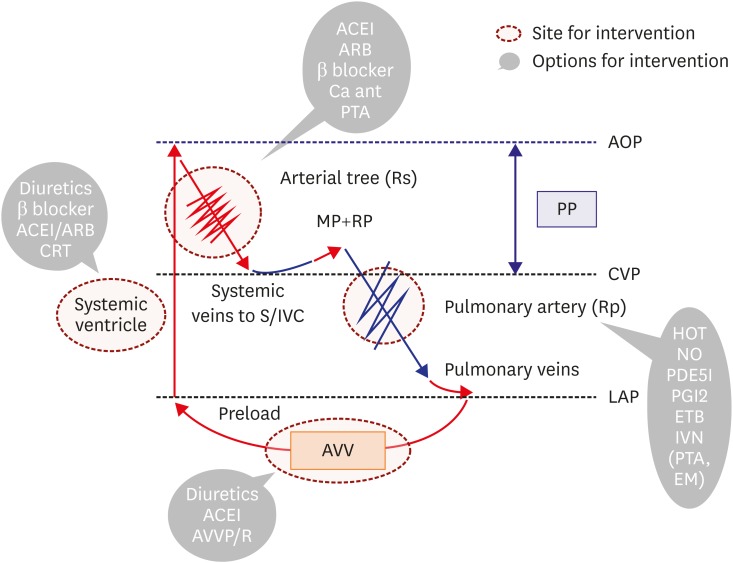
Figure 6.
Traditional failing Fontan hemodynamics (high CVP with low output) and possible therapeutic options. For systemic ventricular systolic dysfunction, conventional anti-HF strategies might be successful. In addition, pulmonary artery dilators could also be effective. For AVV impairment, surgical options should be considered.
ACEI = angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor; AOP = aortic pressure; ARB = angiotensin II receptor blocker; AVV = atrioventricular valve; AVVP/R = atrioventricular valvuloplasty or replacement; CRT = cardiac resynchronization therapy; CVP = central venous pressure; EM = coil embolization to collateral vessels; ETB = endothelin receptor blocker; HF = heart failure; HOT = home oxygen therapy; IVN = catheter intervention; LAP: functional left atrial pressure; MP = muscle pump; NO = nitric oxide; PDE5I = phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor; PGI2 = prostaglandin I2; PTA = percutaneous transluminal angioplasty; RP = respiratory pump; Rp = pulmonary artery resistance; Rs = systemic artery resistance; S/IVC = superior vena cava/inferior vena cava.