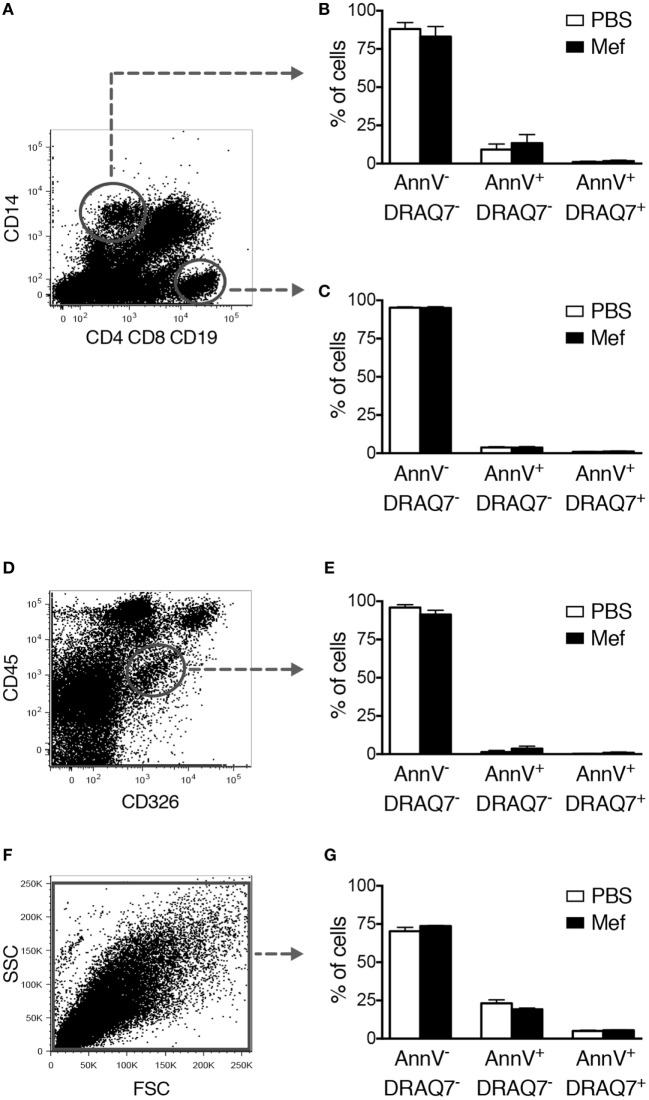
Figure 3.
Mefloquine has no adverse effect on non-mast cell populations of the lung. Mixed human lung cells were prepared by mechanical and enzymatic treatment of lung specimens and were incubated with mefloquine (10 µM) or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) for 24 h and then stained with antibodies recognizing the indicated surface markers. Subsequently, cell death was evaluated by flow cytometry. (A) Representative dot plots showing gated human lung CD14+ cells (monocytes/macrophages) and CD4+ CD8+ CD19+ cells (T/B lymphocytes). (B,C) Quantification of viable (Annexin V−/DRAQ7−), apoptotic (Annexin V+/DRAQ7−), and necrotic (Annexin V+/DRAQ7+) human lung CD14+ (B) or CD4+ CD8+ CD19+ (C) cells (n = 4; representative of two independent experiments/two donors). (D,E) Human lung epithelial cells (CD45− CD326+) were gated (D) and the percentage of viable, apoptotic, and necrotic cells were determined by flow cytometry (E) (n = 3; representative of two independent experiments/two donors). (F,G) Primary human lung smooth muscle cells were incubated with mefloquine or PBS as described above and cell death was evaluated by flow cytometry (n = 3; representative of two independent experiments). All data are presented as mean ± SEM.