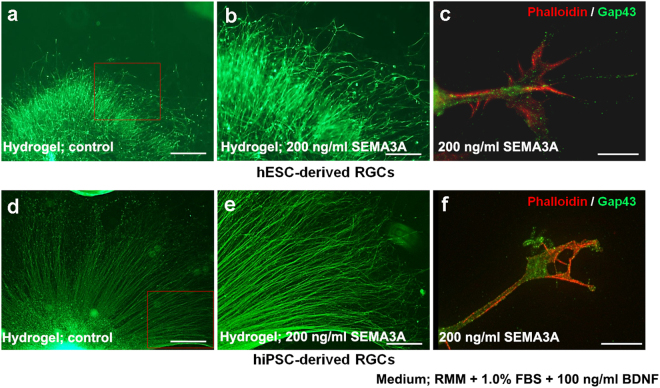
Figure 6.
Effect of locally sustained release of SEMA3A (200 ng/ml) from hydrogels placed in front of attached OVs. Locally sustained release of SEMA3A using hydrogel inhibited anterior axonal growth of hESC- and hiPSC-derived RGCs ((a) and (d), respectively, magnification 40x). In magnified image, most axons are clearly repelled by SEMA3A release ((b) and (e), magnification 100x: squares in (a) and (d), respectively). The filopodia of hESC- and hiPSC-derived RGCs ((c) and (f), respectively) have collapsed owing to SEMA3A release, as evident from phalloidin and GAP43 staining. The assessment from D27 is performed in RMM supplemented with 1.0% FBS and 100 ng/ml BDNF. Each experiment was repeated at least five times. Squares in (a) and (d) correspond to (b) and (c), respectively. Scale bars in (a) and (d), 100 μm. Scale bars in (b) and (e), 40 μm. Scale bars (c) and (f), 10 μm.