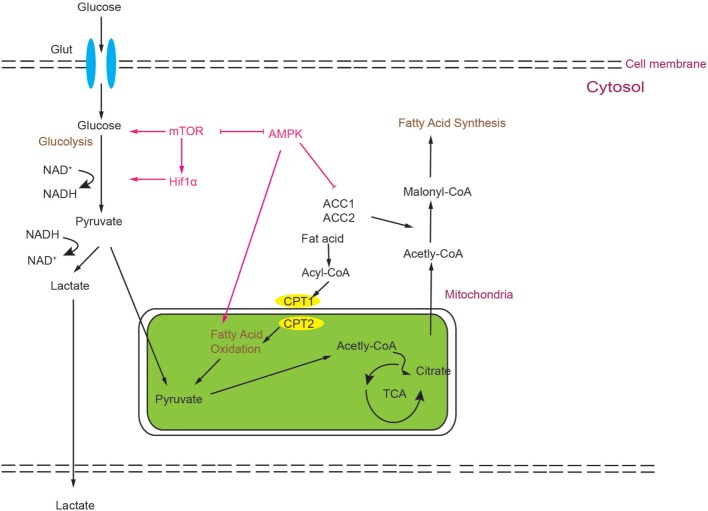
Figure 2.
Simplified scheme of the metabolic processes activated during T cell development. Glucose is imported from the extracellular space by Glut1 and degraded by glycolysis to generate two pyruvate molecules, which can be converted to lactate or Acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA can feed into the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Alternatively, it can also be utilized as a precursor of FAS. Activation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) can modulate HIF1α activity, and both can promote glycolysis. mTOR and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) act as negative regulators for each other. AMPK can inhibit glycolysis and promote fatty acid oxidation.