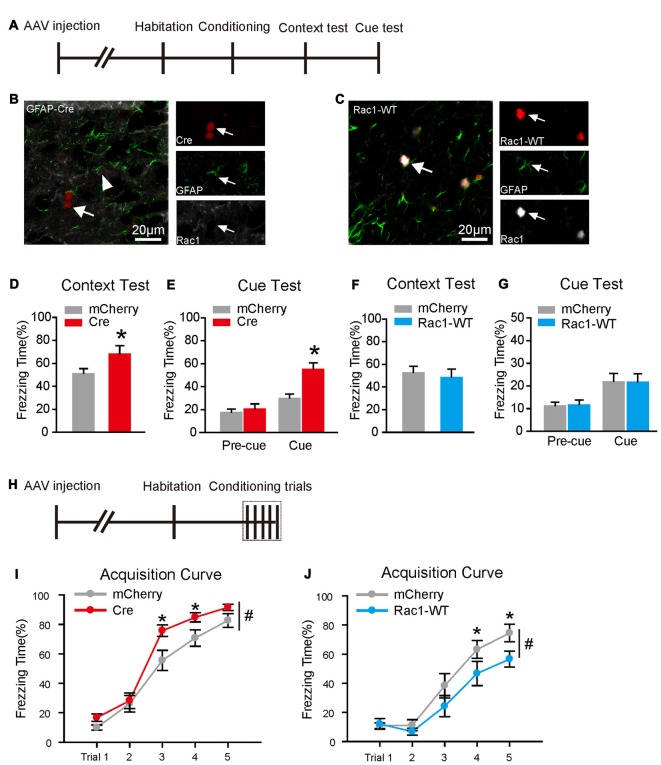
Figure 2.
Astrocytic Rac1 in BLA regulated fear memory acquisition. (A) Experimental design. A single CS-US paired conditioning trial was carried out in Rac1flox/flox mice infected with AAV expressing Cre recombinase and mCherry, or C57 mice infected with Rac1-WT and mCherry. (B) A representative image of Rac1 knockout in astrocyte. White arrows indicate that Rac1 is absent in Cre expressing astrocytes, while strongly expressed in non-Cre Cre expressing astrocytes. (C) Rac1 was strongly expressed in Rac1-WT expressing asrocytes. (D,E) Conditional knockout of astrocytic Rac1 in the BLA before the single CS-US paired conditioning trial increased freezing levels in contextual (D) and cued (E) memory tests (mCherry: n = 12, Cre: n = 8). (F,G) Overexpression of Rac1 in BLA astrocytes had no effect on contextual (F) or cued (G) memory tests (mCherry: n = 9, Rac1-WT: n = 9). (H) Experimental design. Five CS-US paired conditioning trials was carried out in Rac1flox/flox imce infected with AAV expressing Cre recombinase and mCherry, or C57 mice infected with Rac1-WT and mCherry. (I) Conditional knockout of astrocytic Rac1 in the BLA improved fear memory acquisition (mCherry: n = 17, Cre: n = 16). (J) Overexpression of astrocytic Rac1 in the BLA attenuated fear memory acquisition (mCherry: n = 13, Rac1-WT: n = 12). *p < 0.05, #p < 0.05. Scale bar, 20 μm.