Fig. 1.
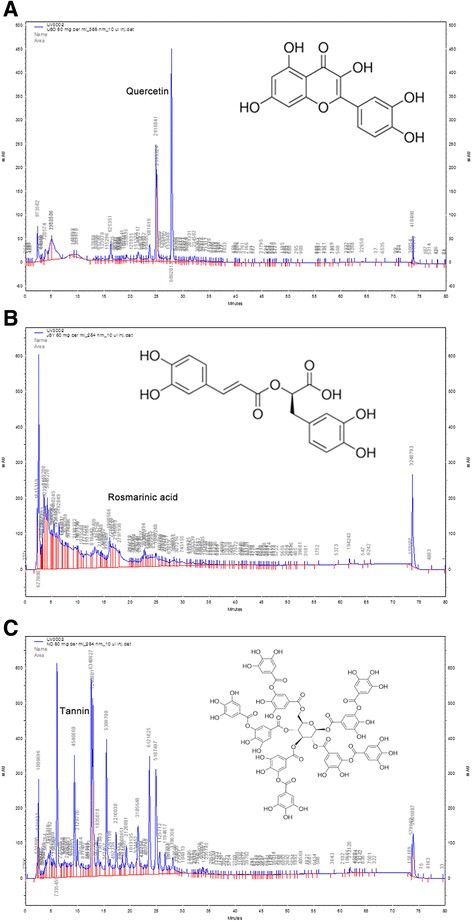
HPLC analysis of each herbal extract component. Chromatographic conditions: SHISEIDO Capcallpak MGII C18 column (4.6 × 250 mm, 5 μm). a HPLC profile of HC at the wavelength of 365 nm. The mobile phase consisted of 0.1% Phosphoric acid in DW (a) and methanol (b), using a gradient elution of 30% B at 0–5 min, 30–90% B at 5–25 min, 90% B at 25–33 min, 90–30% B 33–33.2 min, and 30% B at 33.2–40 min. The solvent flow-rate was 1.0 mL/min and the column temperature was 40 °C. b HPLC profile of PFVA at the wavelength of 254 nm. The mobile phase consisted of 0.05% Phosphoric acid in DW (a) and acetonitrile (b), using a gradient elution of 5–100% B at 0–10 min, 100% B at 10–13 min, and 100–5% B at 13–20 min. The solvent flow-rate was 1.0 mL/min and the column temperature was 35 °C. c HPLC profile of GT at the wavelength of 254 nm. The mobile phase consisted of 0.05% Acetic acid in DW (a) and methanol (b), using a gradient elution of 5–100% B at 0–10 min, 100% B at 10–15 min, and 100–5% B at 15–20 min. The solvent flow-rate was 1.0 mL/min and the column temperature was 35 °C. The contents of quercetin, RA and tannin were determined as 0.14 ± 0.08 mg/g of HC, 17.7 ± 0.80 mg/g of PFVA and 56.74 ± 0.17 mg/g of GT, respectively. HPLC, High performance liquid chromatography; HC, Houttuynia cordata Thunb; PFVA, Perilla frutescens Britton var. acuta; GT, green tea; RA, rosmarinic acid
