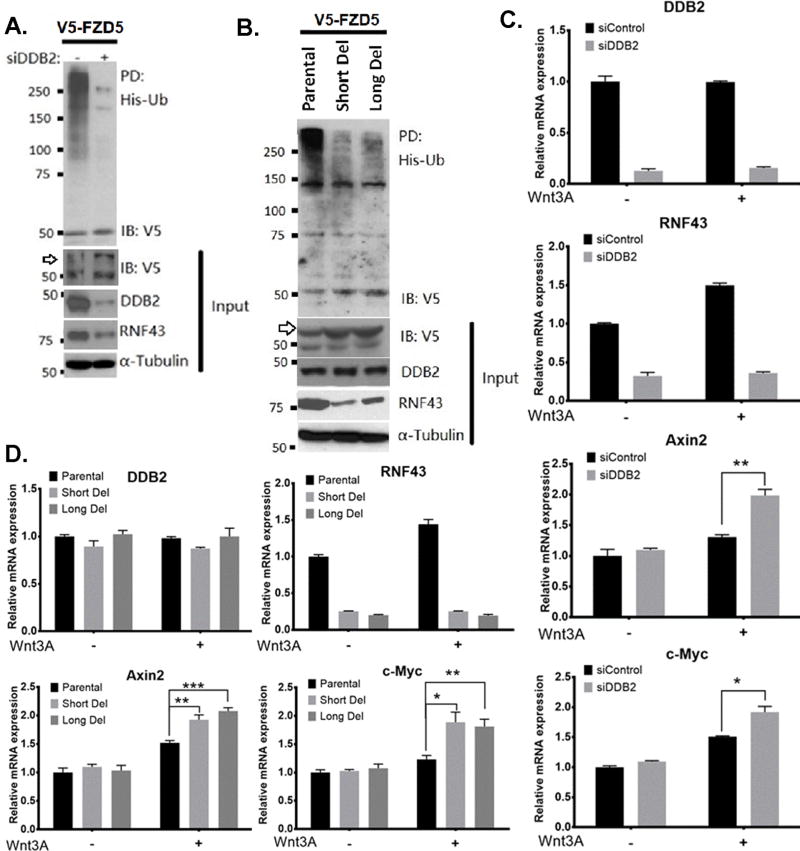
Figure 6. DDB2 is required for RNF43-mediated FZD5 ubiquitination and regulation of the Wnt target genes in colon cancer cells.
(A) DDB2 deficiency leads to inhibition of FZD5 ubiquitination. HT-29 cells were transfected with V5–FZD5, His-ubiquitin and siRNA-Control or siRNA-DDB2, as indicated. His-Ubiquitinated proteins were collected by nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid–agarose beads and the presence of ubiquitinated V5-FZD5 is detected by V5 antibody. (B) Lack of DDB2 bound region in Rnf43gene results in inhibition of FZD5 ubiquitination. HT-29 Parental, Short Del and Long Del cells were transfected with V5–FZD5 and His-ubiquitin. And the assay was performed as described above. IP, Immunopull-down; IB: Immunoblotting; Ub, ubiquitin. Arrows indicate mature, glycosylated V5-conjugated FZD5. (C) HT-29 cells transiently expressing siControl or siDDB2 were treated with vehicle or human recombinant Wnt3A protein (300ng/ml, 24hrs). Relative mRNA levels of DDB2, Rnf43, Axin2 and c-Myc were analyzed using qRT-PCR (Normalized by 18S rRNA). N=3. All error bars indicate SD. (D) Lack of DDB2 binding region in Rnf43gene increases the expression of Wnt/β-catenin pathway target genes upon Wnt3a treatment. HT-29 Parental cells, Short Del cells and Long Del cells were treated with vehicle or human recombinant Wnt3A protein (300ng/ml, 24hrs). Relative mRNA levels of DDB2, Rnf43, Axin2 and c-Myc were analyzed using qRT-PCR (Normalized by 18S rRNA). N=3. All error bars indicate SD. *: P <0.05, **: P <0.01, ***: P <0.001