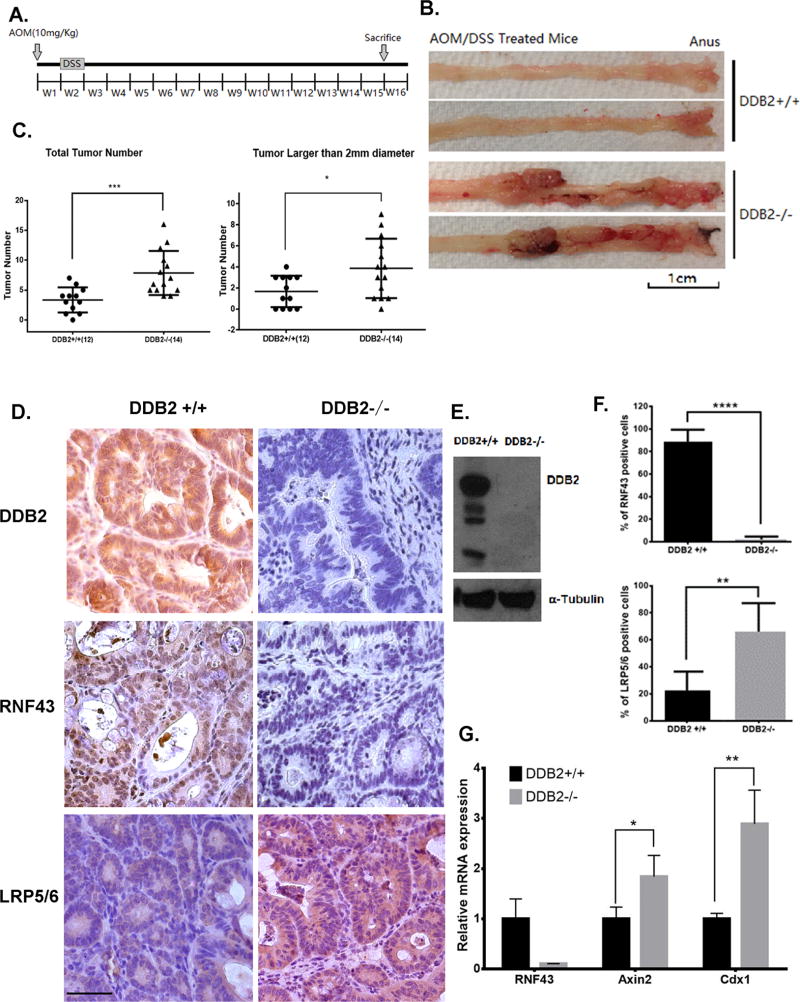
Figure 7. DDB2 deficiency in mouse colon tumors inhibits RNF43 expression and increases abundance of Wnt receptors.
(A) Schematic of the AOM/DSS protocol. Mice were injected with AOM one week prior to beginning the 7-day treatment of DSS. AOM/DSS treated mice were sacrificed 15 weeks after AOM injection. (B) Representative images of mouse colorectum. At 15 weeks, male DDB2+/+ and DDB2−/− mice were sacrificed and the entire colorectal tissues were excised and whole mounts were examined from proximal to distal ends using light microscopy. Increased numbers of nodular and polyploid colonic tumors were observed in the colorectum of the DDB2−/− mice. (C) DDB2 −/− mice developed greater number of tumor nodules than wild-type mice. Quantification of total tumor nodules and the tumors larger than 2-mm diameter observed in 12 DDB2 +/+ mice and 14 DDB2−/− mice. (D) Colorectal tumors from DDB2−/− mice showed significantly decreased level of RNF43 expression and up-regulated level of LRP5/6. Immunohistochemical staining for DDB2, RNF43 and LRP5/6 were performed on the colorectal tissue sections from DDB2+/+ and DDB2−/− mice and images were taken under 40x objective. (Scale bar=50 µm). (E)Western blotting shows the knockout of DDB2 in colon tumor samples. (F) Quantification of the percentage of RNF43 positive and LRP5/6 positive cells. N=15. (G) Upregulated expression of Wnt target genes in DDB2−/− tumors. RNA was extracted from colorectal tumors isolated from DDB2+/+ mice and DDB2−/− mice, and the relative mRNA levels of Rnf43, Axin2 and Cdx1 were examined by qPCR. N=3. All error bars indicate SD. *: P <0.05, **: P <0.01, ***: P <0.001