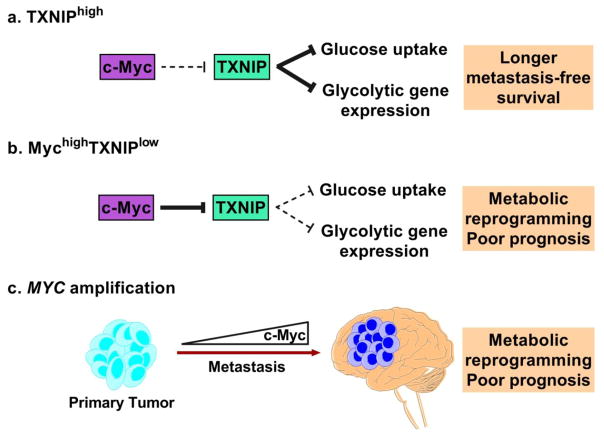
Figure 3. Potential role of c-Myc in metabolic dysregulation.
A) Thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) typically inhibits glucose uptake and glycolytic gene expression. High TXNIP expression is associated with longer metastasis-free survival (46). B) MychighTXNIPlow signature is associated with metabolic reprogramming and poor prognosis in TNBC patients through reduced glucose uptake and glycolytic gene expression. C) MYC amplification is acquired during the metastatic process, which supports a general mechanism of metabolic dysregulation in BMs. This results in an aggressive, glycolytic tumor with a poor prognosis.