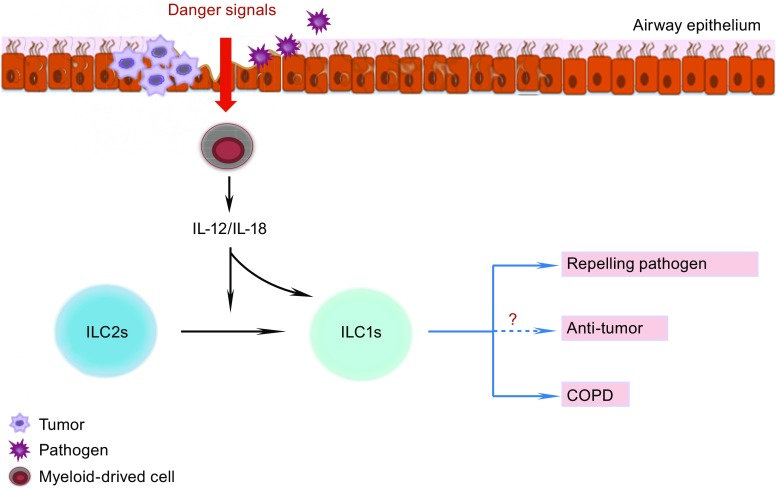
Figure 2.
ILC1 functions in the lung. When pathogens, such as viruses or bacteria, or tumor cells invade the airway epithelium, the myeloid cells receive danger signals from the epithelium and produce IL-12 and IL-18. These pro-inflammatory cytokines down-regulate GATA3 expression of ILC2s and then drive the conversion of ILC2s into ILC1s. IL-12 and IL-18 also enhance the activation and expansion of ILC1s. After activation, ILC1s produce copious amounts of IFN-γ. IFN-γ plays potentially important roles in clearing both pathogens and tumors, and also in the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). See text for details