Figure 4.
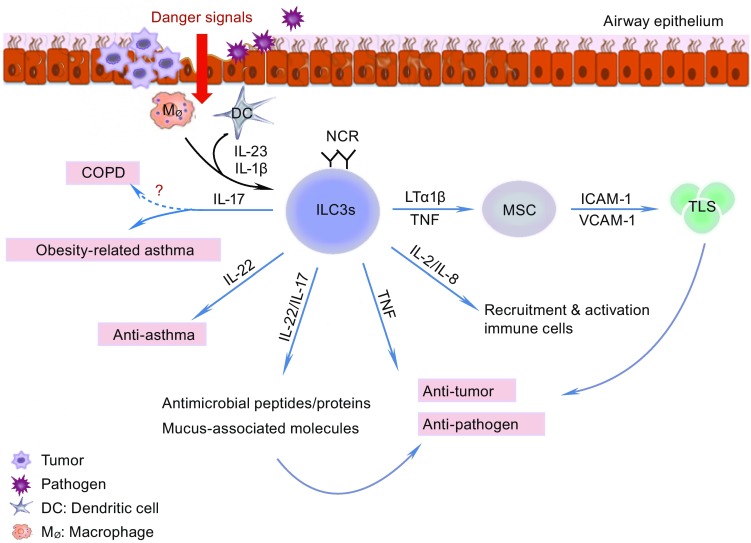
ILC3 functions in the lung. After receiving the danger signals from the airway epithelium upon pathogen and tumor cell invasion, DCs and macrophages release IL-1β and IL-23, which activate ILC3s. Activated ILC3s release IL-17, IL-22, IL-8, IL-2, TNF, and LTα1β2. IL-17 and IL-22 play a dual role: on the one hand, they stimulate the epithelium to produce antimicrobial peptides and proteins, and mucus-associated molecules to clear the pathogen and tumor cells to maintain homeostasis of the mucosa; on the other hand, they may aggravate the development of obesity-related asthma and COPD. IL-22-producing-ILC3s may have anti-asthma effects, whereas IL-17-producing ILC3s may participate in the pathology of asthma, especially in obesity-related asthma. IL-2 and IL-8 recruit neutrophils to the lung. LTα1β2 stimulates mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to express ICAM-1 and VCAM-1. These molecules participate in the formation of a tertiary lymphoid organ in the tumor. See text for details
