Figure 4.
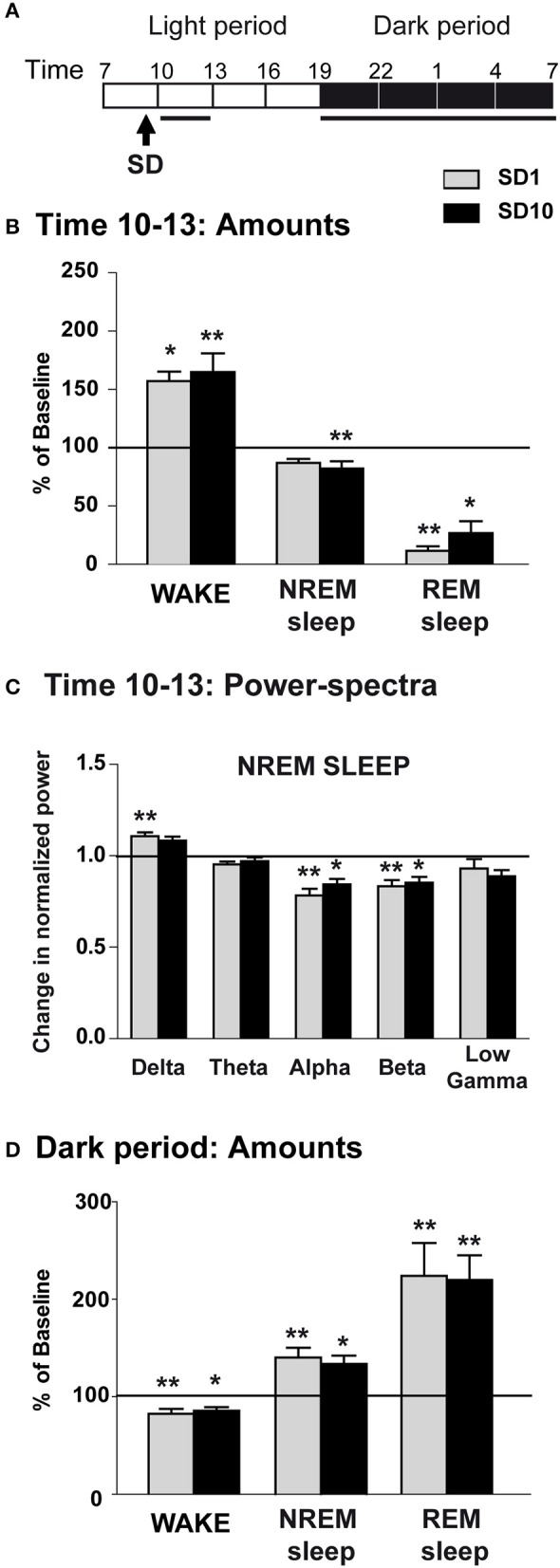
Sleep-wake changes during the first 3 h and the dark period after the social defeat session in unsusceptible mice. (A) Daily experimental timeline. Sleep-wake patterns were analyzed during the first 3-h time window and the 12 h of the dark period after the SD sessions. Power-spectra were analyzed during the first 3-h time window of the light period after the SD session. Analyzed time windows are indicated by black bars above the respective recording days (SD1 and SD10). (B) Amounts of wake, NREM sleep and REM sleep expressed as minutes per 3 h on days SD1 and SD10 in unsusceptible mice (n = 7). Sleep-wake states were analyzed for the first 3-h time window after the SD session (starting at 9:30 a.m.) and compared to results obtained from BL recordings. Data are expressed as percentage of BL and absolute values at BL (corresponding to 100%) were, in minutes per 3 h: 49 ± 4 (wake), 119 ± 4 (NREM sleep) and 11.9 ± 0.9 (REM sleep). (C) Changes in normalized EEG power spectrum on days SD1 and SD10 compared to BL during NREM sleep in unsusceptible mice (n = 7). Changes in normalized EEG power in each power band (delta: 0.5–4.99 Hz, theta: 5–9.9 Hz, alpha: 10–12.99 Hz, beta: 13–29.99 Hz, and low gamma: 30–50 Hz) were expressed as a ratio of individual relative values obtained on each SD session over BL. For each mouse, relative values were obtained by dividing each power band over the sum of all values from 0.5–50 Hz. (D) Amounts of wake, NREM sleep and REM sleep expressed as minutes per 12 h of the dark period on days SD1 and SD10 in unsusceptible mice (n = 7). Sleep-wake states were analyzed for the 12 h of the dark period following the SD session (starting at 9:30 a.m.) and compared to results obtained from BL recordings. Data are expressed as percentage of BL and absolute values at BL (corresponding to 100%) were, in minutes per 12 h of the dark period: 490 ± 12 (wake), 215 ± 10 (NREM sleep) and 14.6 ± 2.3 (REM sleep). All data are expressed as means ± SEM of seven unsusceptible mice. Statistical analysis was performed on absolute values. For multiple group comparisons: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, significantly different from the control conditions (BL); for statistics see Table S1.
