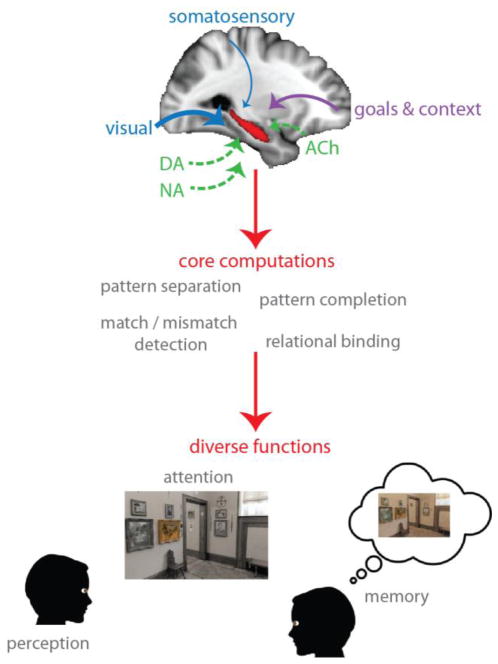
Figure 1.
Top: Multiple sensory modalities, including vision, audition, somatosensation, and olfaction, converge on the hippocampus. These inputs can be flexibly weighted based on behavioral goals and task context, which themselves are represented elsewhere, such as in frontoparietal cortex. In this example, visual signals are up-weighted (thicker arrow) while somatosensory signals are down-weighted (thinner arrow). Neuromodulatory systems, including dopaminergic (DA), cholinergic (ACh), and noradrenergic (NA) systems, can bias this flow of information and local processing. Middle: The hippocampus performs a core set of domain-general computations. Bottom: Flexibly weighted inputs, combined with some or all of these computations, enable the hippocampus to contribute to various cognitive functions.