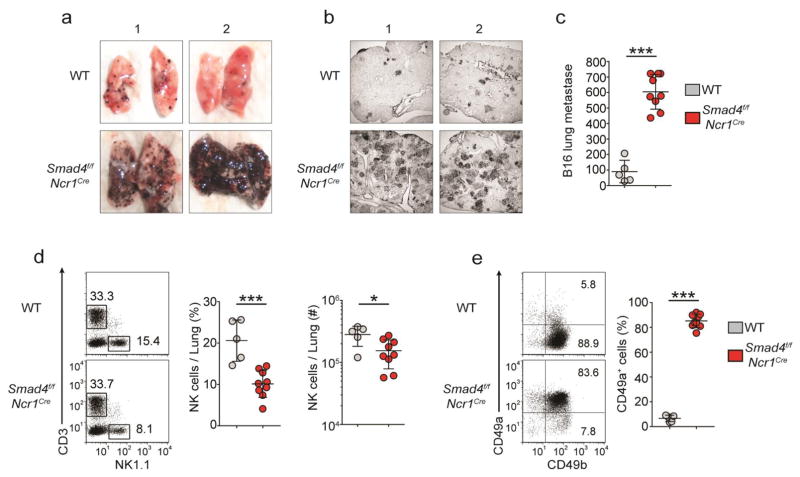
Figure 2.
SMAD4 is essential for NK cell–mediated anti-tumor immunity. (a,b) Images of whole lungs (a) and microscopy of tissue sections (12 μm thick) of a single lung lobe (b) from Smad4f/f and Smad4f/fNcr1iCre mice (two per genotype shown, 1,2 above images) 15 d after intravenous injection with 1 × 105 B16 cells. Original magnification (b), ×2.5. (c) Quantification of total black B16 foci on the surface of lungs of mice as in a. (d) Flow cytometry (left), frequency (middle) and absolute number (right) of lung NK cells from mice as in a,b. Numbers adjacent to outlined areas (left) indicate percent T cells (CD3+NK1.1−, top left) or NK cells (CD3−NK1.1+ cells, bottom right). (e) Expression of CD49a and CD49b in lung NK cells from mice as in a. Each symbol (c–e) represents an individual mouse; small horizontal lines indicate the mean (± s.d.). *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001 (unpaired Student’s t-test). Data are pooled from two independent experiments.