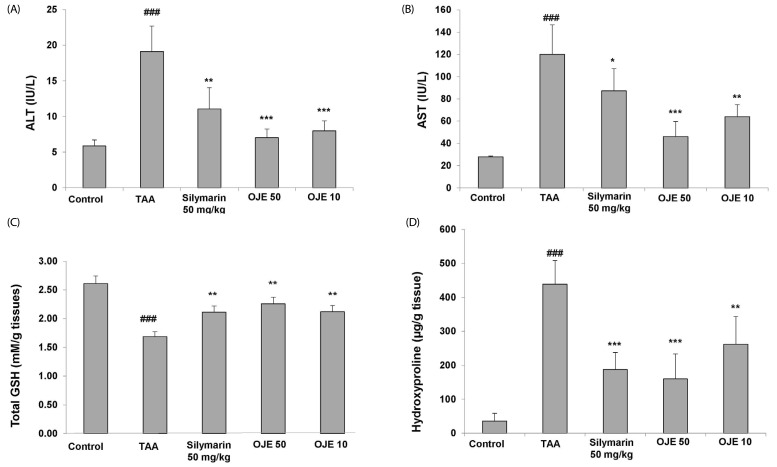
Fig. 4. Effect of OJE on AST/ALT levels, total glutathione (GSH) contents and hydroxyproline levels in TAA-induced liver fibrosis rats.
A: HSC-T6 cells were incubated with 10 and 50 mg/mL OJE for 24 h. Expression of fibrosis related genes in HSC-T6 cells was determined by real-time PCR. The results are expressed as normalized fold values relative to the control. Levels of ALT (A) and AST (B) in serum were measured by spectrophotometry. (C) Total GSH contents in liver tissue (D) and hydroxyproline levels of TAA-induced liver tissue of rats were measured using spectrophotometry. TAA, thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis rats; Silymarin, positive control rats; OJE 10, TAA plus OJE 10 mg/kg treated rats; OJE 50, TAA plus OJE 50 mg/kg treated rats. Data are expressed as means ± SEM (n = 8) which were compared using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Student's t-test. ###P < 0.001 compared to the control group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with TAA group. OJE, O. japonica extract; TAA, thioacetamide; ALT, alanine transaminase; AST, aspartate transaminase; GSH, glutathione.