Fig. 2.
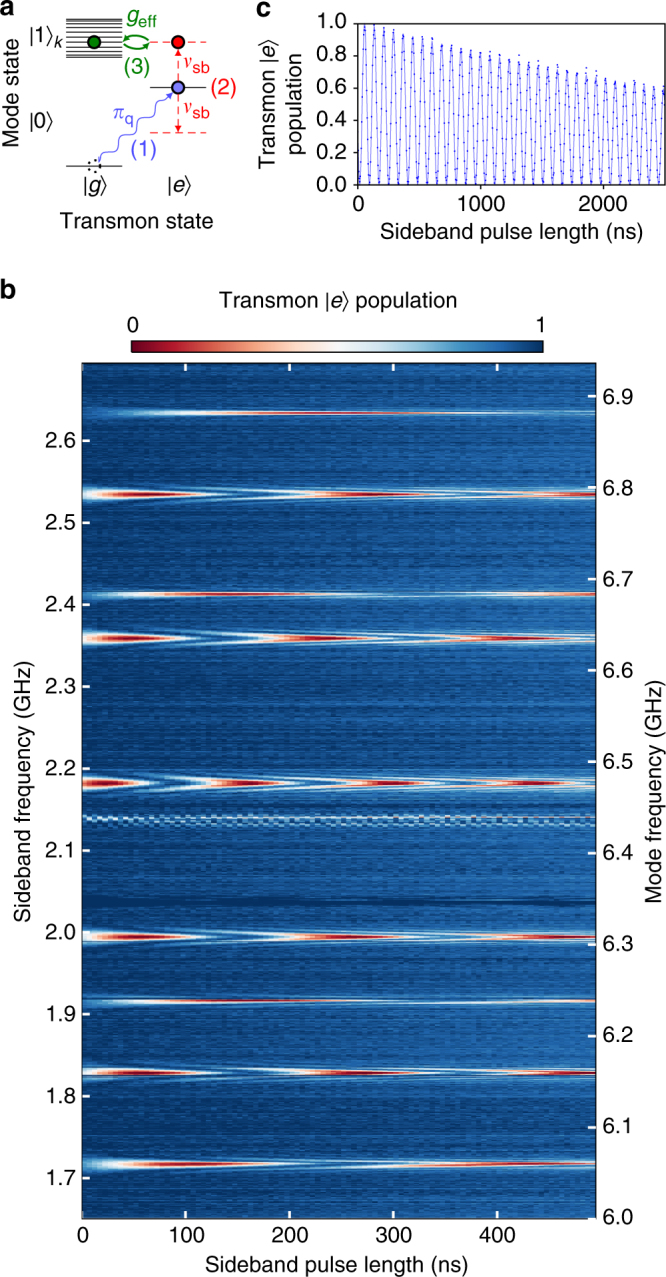
Stimulated vacuum Rabi oscillations. a Generation of stimulated vacuum Rabi oscillations. is the state with a single photon in mode k; all other modes are in the ground state. (1) An excitation is loaded into the transmon via its charge bias. (2) The transmon frequency is flux-modulated to create sidebands. (3) When a sideband is resonant with a mode, single-photon vacuum Rabi oscillations occur between transmon and the mode. b Experimental results obtained from this protocol for a range of sideband modulation frequencies, with the transmon biased at v q = 4.28 GHz. The length of the flux modulation pulse is swept for each frequency and the excited state population of the transmon is measured after the pulse ends. Chevron patterns indicate parametrically induced resonant oscillations with each of the memory modes. Two of the eleven modes are weakly coupled to the transmon and are not visible at these flux modulation amplitudes. The distribution of the modes can be understood through Hamiltonian tomography48 (Supplementary Note 9). c Resonant oscillations between transmon and mode 6
