Fig. 4.
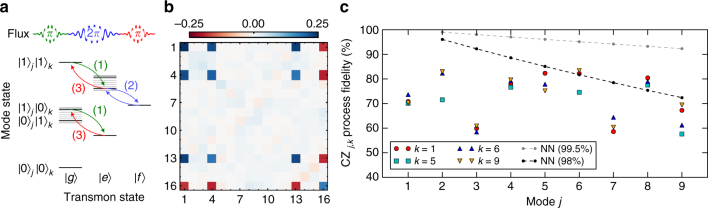
Controlled-phase gate between two arbitrary modes. a Protocol for controlled-phase (CZ) gate between an arbitrary pair of modes, with j indicating the control mode and k indicating the target mode of the gate: (1) The state of mode j is swapped to the transmon via a transmon-mode iSWAP pulse at the frequency difference between the transmon transition and mode k. (2) A CZ gate is performed between mode k and the transmon, by applying two frequency-selective iSWAPs from energy level to level and back, mapping the state to . (3) The state of the transmon is swapped back to mode j, reversing the iSWAP in (1). b Process matrix for the CZ gate between modes j = 6 and k = 8, corresponding to a process fidelity of 82% (see Supplementary Note 17 for details on state preparation and measurement). c Fidelities from process tomography for 38 pairs of memory modes with k = 2, 5, 6, 8. The process fidelities are extracted from sequences that include SPAM errors, and are conservative estimates of the gate fidelities. For comparison, the dashed black and gray lines show the decay in fidelity for a two-qubit gate between qubit 1 and qubit j in a corresponding linear array comprising only nearest-neighbor gates with fidelities of 99.535 and 98%, respectively