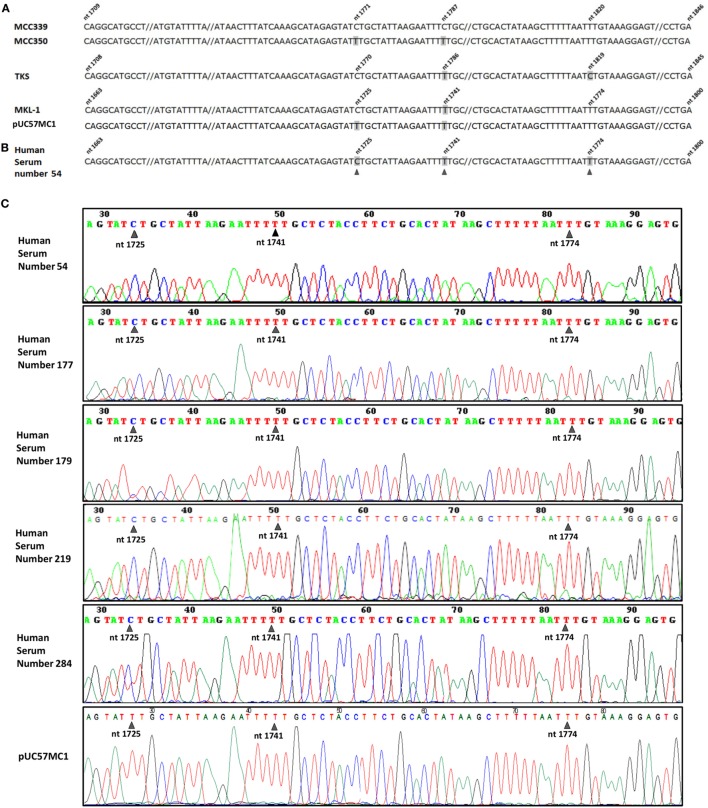
Figure 2.
Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCPyV) sequence analysis. (A) MCPyV large T antigen (LT) sequences alignment of four MCPyV genotypes, Merkel cell carcinomas (MCC)339 (GenBank, accession number EU375804.1), MCC350 (GenBank, accession number EU375803.1), TKS (GenBank, accession number FJ464337), MKL-1 (GenBank, accession number FJ173815), together with the recombinant plasmid pUC57MC1, which contains MCC350 LT sequences (17, 20). The four aligned MCPyV DNA sequences, representing the same LT region, show different nucleotide numeration due to upstream nucleotide deletion (not shown) in their genome. Nucleotide substitutions in MCPyV strains are numbered and marked in gray. (B) DNA sequences of the MCPyV-positive sample, number 54. Five out of 190 DNA samples from serum samples contain single nucleotide substitutions (black arrow heads), which are cumulatively marked in gray in the representative MCPyV DNA sequences of sample 54. (C) MCPyV DNA sequences detected in human serum samples, numbers 54, 177, 179, 219, 284, contain a single nucleotide substitution at nt 1,725 (black arrow heads), corresponding to MKL-1 genotype, as shown in (A), fourth line.