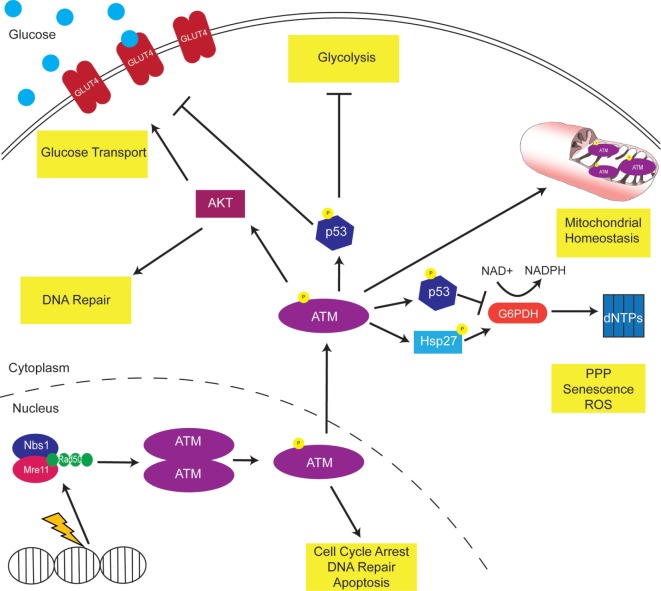
Figure 1.
Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM) modulates cellular metabolism. DNA damage activates ATM to phosphorylate multiple downstream proteins regulate cell cycle arrest, DNA repair, and apoptosis pathways. A non-canonical function of ATM is the regulation of cellular metabolism. Mitochondrial ATM acts to regulate mitochondrial homeostasis by repairing mitochondrial genome defects. ATM activates the tumor suppressor p53, which inhibits GLUT recruitment, glycolysis, and dNTP production. Consistently, p53 targets the oncogene c-myc, inhibiting the TCA cycle and increasing the Warburg effect. In addition, ATM activates AKT to increase GLUT recruitment to the membrane.