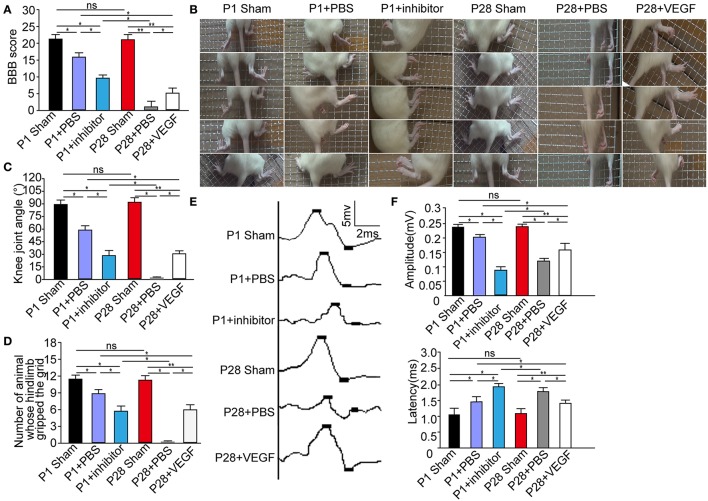
Figure 2.
VEGF treatment improves locomotor recovery in rats after complete ST. (A) The BBB scores in the P28 + PBS group were significantly lower than those in P1 + PBS, P28 + VEGF, and P28 sham groups; the scores in the P1 + inhibitor group were also significantly lower than those in P1 + PBS and P1 sham groups but higher than those in the P28 + PBS group; (B) In grid climbing test, continuous time-lapse images from the video showed alternative movements of two hindlimbs, involving the flexion and extension of the three major joints (the hips, the knees, and the ankles) in sham and P1 + PBS groups but not in the P28 + PBS groups. In P28 + VEGF and P1 + inhibitor group, slight movements of two or three joints were found; (C) The knee joint angles were assessed in six groups: the value of knee joint angle was significantly decreased in P1 and P28 ST rats compared with that in sham groups, was higher in the P28 + VEGF group than that in the P28 + PBS group, and was lower in the P1+ inhibitor group than that in the P1 + PBS group; (D) The number of animals whose hindlimb gripped the grid was shown in six groups; (E) SMEPs were recorded in six groups: P1 sham, P1 + PBS, P1 + inhibitor, P28 sham group, P28 + PBS, and P28 + VEGF groups; (F) SMEPs significantly decreased in P1 and P28 ST rats compared with that in sham rats. The peak value of the amplitude significantly reduced in P1 rats with the inhibition of VEGF compared with that in the P1 + PBS group. The peak value of amplitude significantly increased in P28 rats treated with VEGF compared with that in the P28 + PBS group. The changes in the latency showed an opposite trend to that of the amplitude in these groups. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; n = 12 in each group.