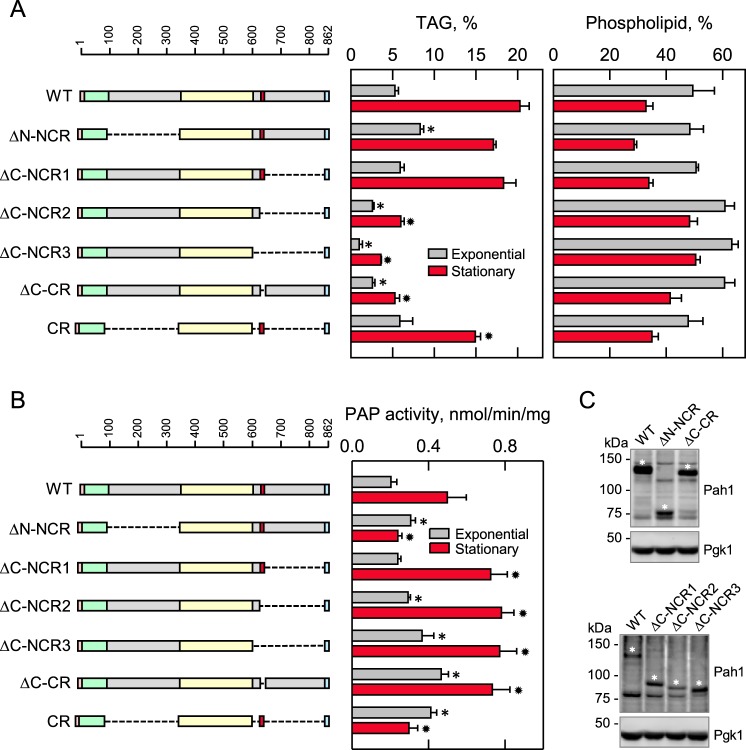
Figure 5.
Effects of N- and C-terminal region mutations of Pah1 on TAG content and PAP activity. The indicated wild-type and mutant forms of Pah1 were expressed from pGH315-based plasmids (Table 1) in the pah1Δ mutant strain SS1026 (A) or the pah1Δ app1Δ dpp1Δ lpp1Δ quadruple mutant strain GHY66 (B and C). The cells were grown to the exponential and stationary phases of growth in SC−Leu medium with (A) or without (B) [2-14C]acetate (1 μCi/ml) at 30 °C. A, lipids were extracted and separated by TLC, and the phosphor images were subjected to ImageQuant analysis. The percentages shown for TAG and phospholipids were normalized to the total 14C-labeled chloroform-soluble fraction. B, cells were harvested by centrifugation, cell extracts were prepared, and PAP activity was measured by following the release of 32Pi from 32P-labeled PA. C, samples (50 μg of protein) of cell extracts from exponential phase cells were subjected to immunoblot analysis using 2 μg/ml anti-Pah1 antibodies raised against the C-terminal (top blot) or N-terminal (bottom blot) portions of Pah1 and anti-Pgk1 antibodies. The asterisks designate the positions of the wild-type and mutant forms of Pah1. The anti-Pah1 antibodies cross-react with proteins other than Pah1 (e.g. bands below (top blot) and above (bottom blot) the 75 kDa marker. The CR mutant was not detected with the anti-Pah1 antibodies. The data in A and B are means ± S.D. (error bars) from triplicate determinations of two independent experiments, whereas the immunoblots shown in C are representative of three independent experiments. The positions of the amino acid residues of full-length Pah1 are shown (A and B, top left). The color code for the domains of Pah1 is as indicated in the legend to Fig. 1. *, p < 0.05 versus WT exponential phase. *, p < 0.05 versus WT stationary phase.