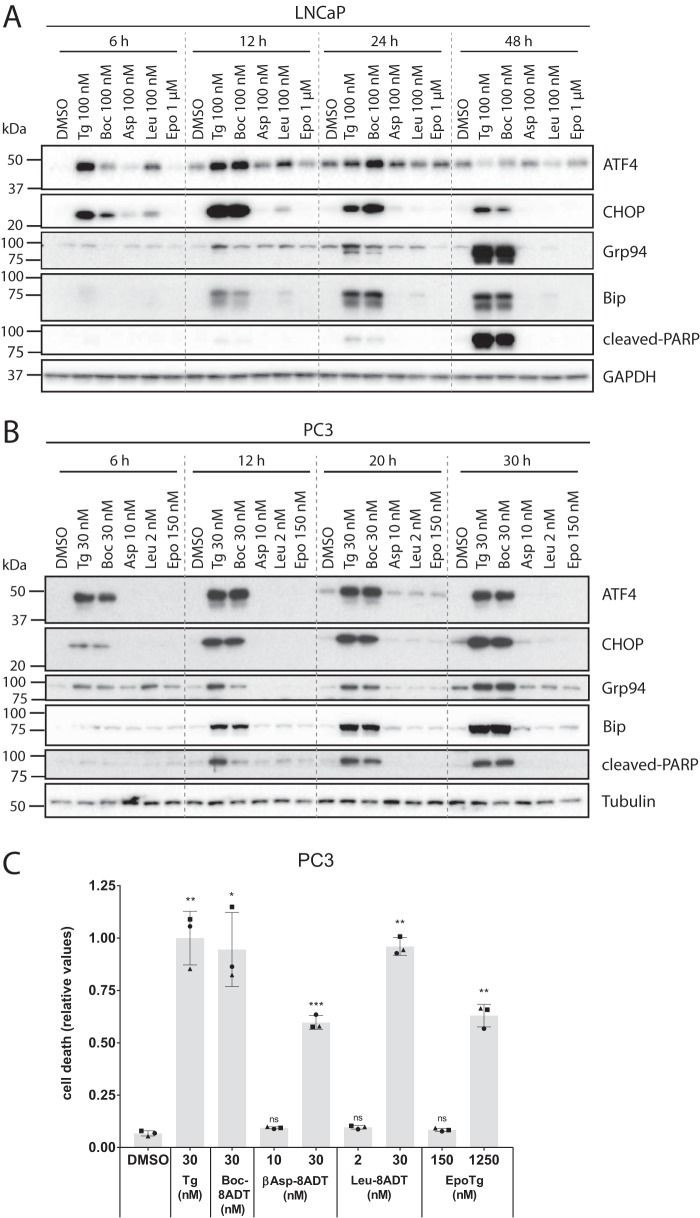
Figure 9.
Only toxic concentrations of Tg and Tg analogs induce a sustained UPR. LNCaP (A) or PC3 (B) cells were seeded in 6-well plates and grown for 2 days upon which they were treated for four different time points (as indicated) with toxic concentrations of Tg or Boc-8ADT (100 nm in LNCaP and 30 nm in PC3) or with low/subtoxic concentrations of βAsp-8ADT (100 nm in LNCaP and 10 nm in PC3), Leu-8ADT (100 nm in LNCaP and 2 nm in PC3), or EpoTg (1 μm in LNCaP and 150 nm in PC3). Protein lysates were prepared and analyzed by immunoblotting to assess the expression levels of the indicated proteins (ATF4, CHOP, Grp94, and BiP as UPR indicators and cleaved PARP as a marker for caspase activity). GAPDH and tubulin were used as loading controls. The dotted lines are inserted for visual aid only (i.e. the membranes were not spliced). One representative experiment of three independent experiments is shown for each cell line. The positions of molecular mass markers are indicated to the left of the blots. C, PC3 cells were seeded in 96-well plates and incubated for 2 days. Subsequently, the cells were treated with DMSO control or the indicated concentrations of Tg, Boc-8ADT, βAsp-8ADT, Leu-8ADT, or EpoTg together with 2.5 μg/ml propidium iodide in complete medium. Cell death was assessed using an Incucyte instrument for automated live-cell imaging and calculation of red fluorescence and total cell confluence. Cell death is plotted as the ratio of red fluorescence to total cell confluence after 48 h, normalized to that obtained with Tg. Data are means ± S.E. from three independent experiments with error bars representing S.E. Single symbols represent individual measurements (each symbol represents the mean value from triplicate wells), and each experiment is indicated by differently shaped symbols. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ns, not significant (i.e. p ≥ 0.05), paired Student's t test compared with DMSO control.