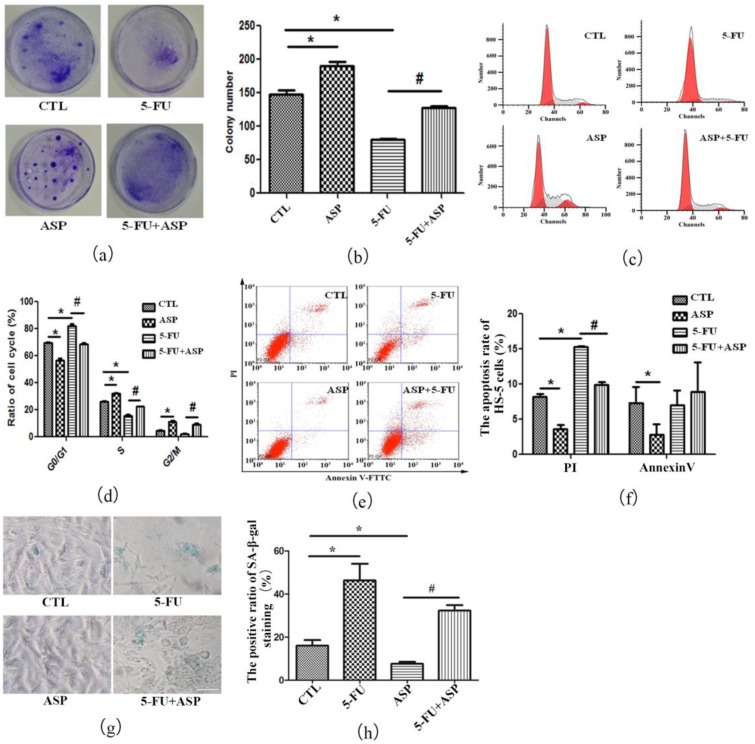
Figure 2.
Angelica sinensis polysaccharide (ASP) rescues HS-5 cell growth inhibition after 5-FU treatment via anti-apoptosis and anti-senescence effects. (a) HS-5 cells treated with 5-FU, ASP, or a combination of both were cultured for 12 days, then stained by 0.5% crystal violet. CFU-F clusters are blue stained in dishes; (b) CFU-F frequency in different groups is presented as means ± SD; (c) Representative flow cytometry graphs of cell cycle analysis of HS-5 cells are shown; (d) The results of cell cycle distribution of HS-5 cells are presented as means ±SD; (e) Annexin V/Propidium iodide (PI) staining was employed to detect apoptotic HS-5 cells by flow cytometry. In each chart, upper left represents necrotic cells; bottom left represents vital cells; upper right represents intermediate-stage and late-stage apoptotic cells; and bottom right represents early-stage apoptotic cells; (f) The percentage of apoptotic HS-5 cells in different groups is presented as means ± SD. The left panel represents the ratio of intermediate-stage and late-stage apoptotic cells positively stained by PI. The right panel represents the ratio of early-stage apoptotic cells positively stained by Annexin V; (g) Senescence-related SA-β-gal staining was employed to detect senescent HS-5 cells. Senescent cells are blue-green stained (Scale bar = 50 μm); (h) The positive ratio of SA-β-gal staining is presented as means ± SD. * p < 0.01 vs. control group, # p < 0.01 vs. 5-FU group.