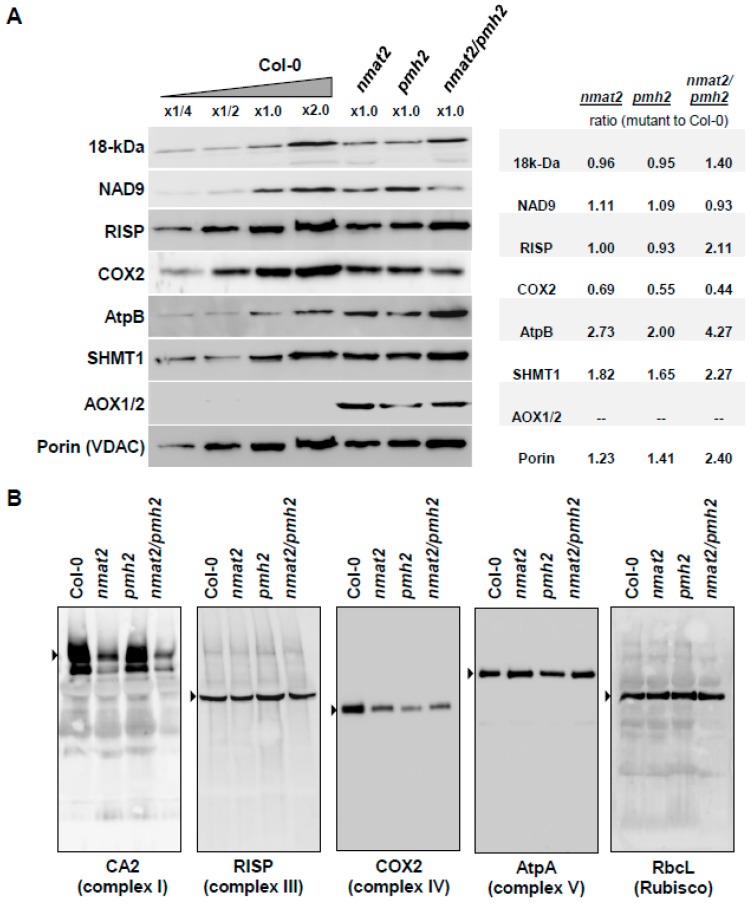
Figure 6.
Relative accumulation of organellar proteins in wild-type plants and nmat2, pmh2 and nmat2/pmh2 mutants. (A) Immunoblots with total proteins (about 50 μg) extracted from three-week-old rosette leaves of wild-type plants, and homozygous nmat2 and pmh2 mutants. The blots were probed with polyclonal antibodies raised to γ-carbonic anhydrase-like subunit 2 (CA2), NADH-oxidoreductase subunit 9 (NAD9) and the 18-kDa subunits of complex I, Rieske iron-sulfur protein (RISP) of complex III, the cytochrome oxidase subunit 2 (COX2) of complex IV, mitochondrial ATP-synthase subunits and (AtpA and AtpB) of complex V, serine hydroxymethyltransferase 1 (SHMT1) protein and the mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC, or Porin). Detection was carried out by chemiluminescence assays after incubation with HRP-conjugated secondary antibody; (B) BN-PAGE of crude mitochondria preparations was performed according to the method described previously [83]. Crude mitochondria preparations, obtained from three-weeks old Arabidopsis seedlings, were solubilized with DDM (1.5% (w/v)) and the organellar complexes were resolved by BN-PAGE. For immunodetections, the proteins were transferred from the native gels onto a PVDF membrane. The membranes were distained with ethanol before probing with specific antibodies (Table S3), as indicated below each blot. Arrows indicate to the native complexes I (~1000 kDa), III (dimer, ~500 kDa), IV (~220 kDa) and V (~600 kDa).