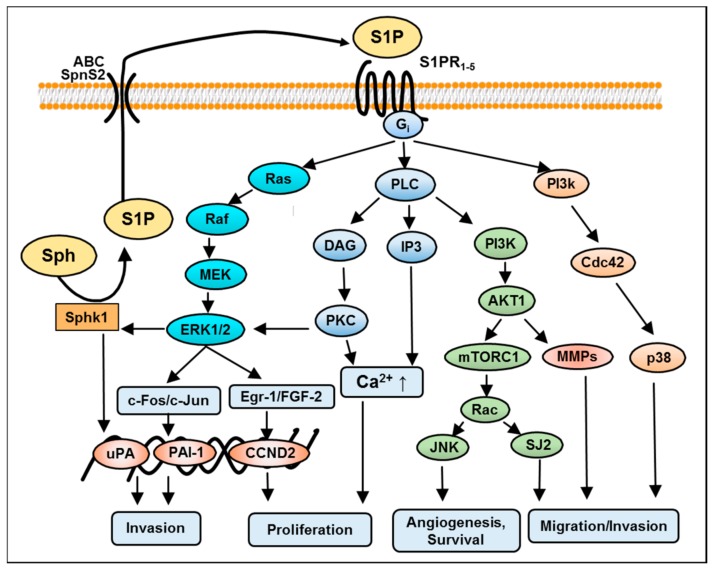
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram depicting guanine nucleotide-binding protein (Gi)-mediated S1PRs activation and multiple signaling pathways in glioblastoma. S1PRs via stimulation of the Gi may simultaneously activate MAPK-ERK1/2, c-jun N-terminal kinases (JNK), phospholipase C (PLC), phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and p38 pathways in glioma cells. Following the activation of downstream signaling, ERK1/2 facilitates the co-expression and activation of c-jun, c-fos and the early growth response (Egr-1)/fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2) system respectively. Cell cycle arrest by CCND2 (cyclin D2) gene expression and the PLC/Ca2+ system is responsible for proliferation. Sphingosine kinase 1 (SphK1) signaling is necessary for the maintenance of urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) expression and the basal invasive activity of glioma cells by a receptor-independent mechanism. While phosphorylation of SphK1 by ERK1/2 regulates S1P production and spiral signaling PI3k/ATK pathways through the activated downstream targets, mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) and metalloproteases (MMPs) lead to angiogenesis and survival. On the other hand, p38 signaling induces migration. Additional abbreviations used in the figure are defined as follows: DAG, diacylglycerol; ERK1/2, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2; Gi, guanine nucleotide-binding protein; IP3, inositol-1, 4, 5-triphosphate; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PKC, protein kinase C; PLC, phospholipase C; ↑, increased.