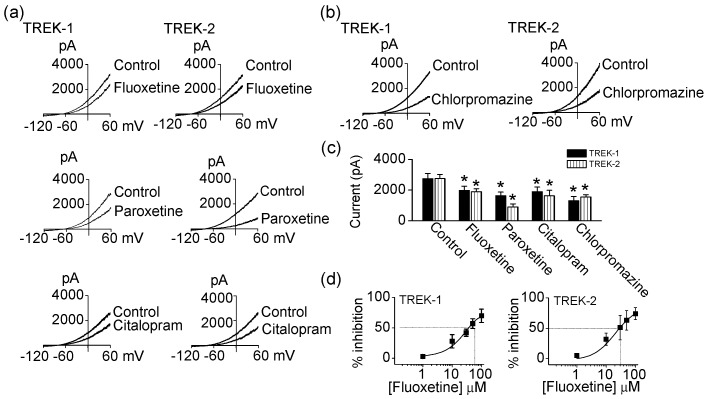
Figure 1.
Effect of antidepressants and antipsychotics on TWIK-related K+ (TREK) channels. (a) Inhibition of TREK currents by fluoxetine, paroxetine, and citalopram. Whole-cell currents were recorded from HEK-293A cells expressing TREK-1 and TREK-2 before and after application of antidepressants. Cell membrane potential was held at −80 mV, and ramp pulses were applied from −120 mV to +60 mV. Pipette solution contained 150 mM KCl and bath solution contained 5 mM KCl and 135 mM NaCl; (b) Inhibition of TREK currents by chlorpromazine. Same protocol for recording of whole-cell currents as in a; (c) Summary of effect of fluoxetine (TREK-1, n = 10; TREK-2, n = 6), paroxetine (TREK-1, n = 10; TREK-2, n = 7), citalopram (TREK-1, n = 10; TREK-2, n = 7), and chlorpromazine (TREK-1, n = 4; TREK-2, n = 16) on TREK currents. Each bar is the mean ± standard deviation (SD ) of five experiments. Asterisk (*) indicates a significant difference against the control without application of fluoxetine, paroxetine, citalopram, or chlorpromazine (p < 0.05); (d) Dose-dependent effect of fluoxetine on TREK-1 (n = 8) and TREK-2 (n = 4) current. The inhibition of TREK current by increasing concentrations of fluoxetine (1 to 100 μM).