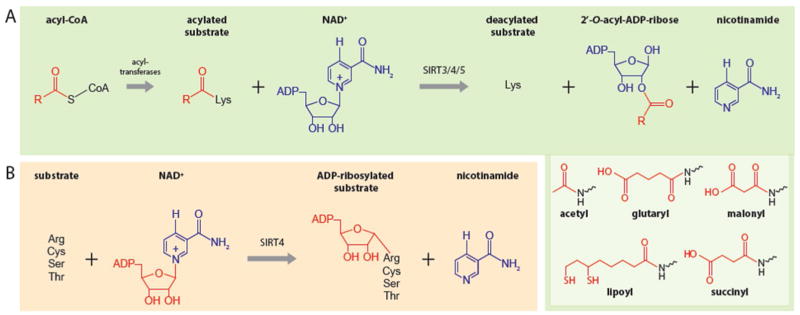
Figure 1. Mitochondrial Sirtuins Are NAD+-Dependent Deacylases and ADP-Ribosyl Transferases.
A. mitochondrial sirtuins remove acyl moieties by positioning NAD+ to nucleophilically attack the acylated lysine. As a result, NAD+ is cleaved and 2′-O-acyl-ADP ribose and nicotinamide are formed in the process. The best characterized acyl modifications removed by mitochondrial sirtuins are shown in the inset. B. SIRT4 catalyzes the transfer of ADP-ribose from NAD+ to arginine, cysteine, serine and threonine substrates. Here, NAD+ is used by SIRT4 to nucleophilically attack the substrate yielding nicotinamide as a byproduct.