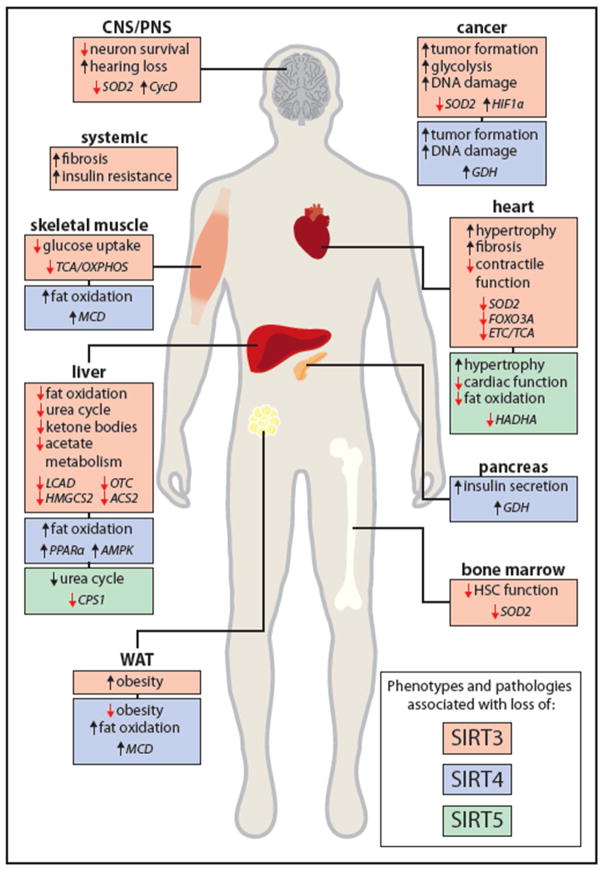
Figure 3. Loss of SIRT3, SIRT4 and SIRT5 Can Cause Age-Related Pathologies.
Loss of SIRT3 (red), SIRT4 (blue) and SIRT5 (green) have been associated with the development of age-related diseases including cardiopathologies, insulin resistance, reduced immune function and neurodegeneration. The major phenotype associated with loss of the specific mitochondrial sirtuin is described per organ system together with the identified substrates (italicized) responsible for the development of the disease. See the section “Mitochondrial Sirtuins Protects Against Age-Related Diseases” for more detail on the different sirtuin substrates and phenotypes associated with loss of sirtuin function. WAT: white adipose tissue, CNS: central nervous system. PNS: pheriperal nervous system.