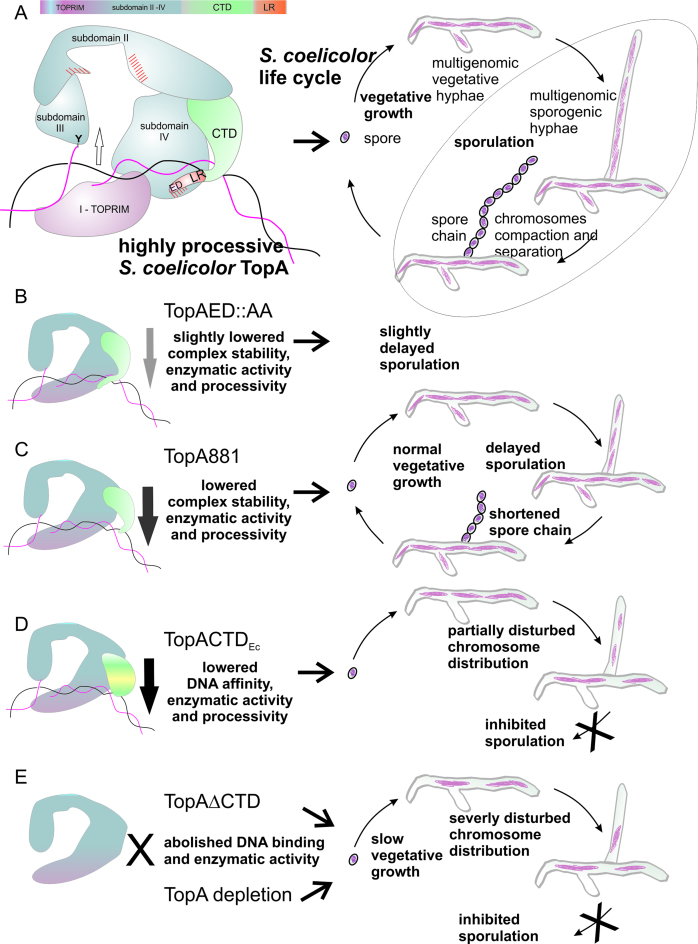
Figure 6.
Model of DNA complex formation by the S. coelicolor TopA. (A) A speculative model of the TopA–DNA complex that involves the formation of the DNA-stabilizing clamp by the CTD, fastened due to the interaction between the lysine repeats (LR, red) with DNA and actinobacterial unique sequence (red hatched area) in subdomain IV. (B–E) The influence of TopA modifications—exchange of C-terminal Glu and Asp for Ala (TopAED:AA) (B); truncation of the lysine repeats (TopA881) (C); the fusion of E. coli TopA C-terminal domain (TopACTDEc) (D) and the CTD truncation (TopAΔCTD) (E)—on DNA binding, enzymatic activity, and processivity is reflected in in vivo functionality either during sporulation alone or also during vegetative growth.