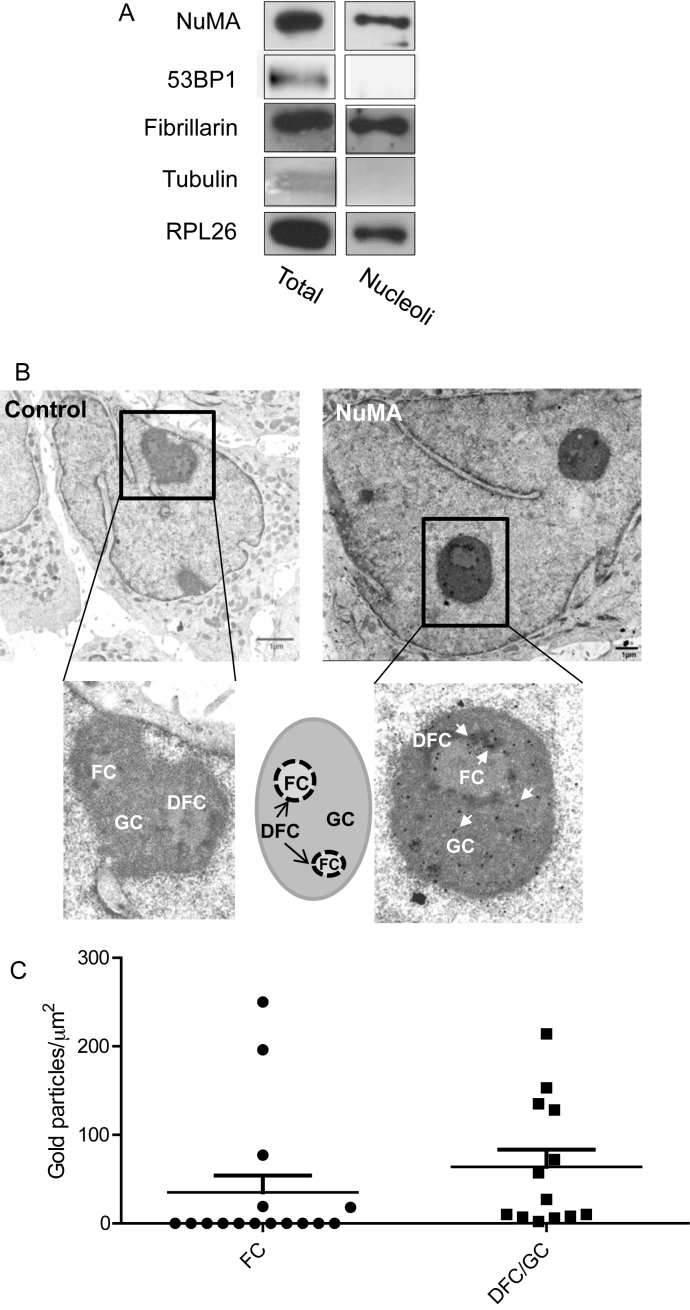
Figure 1.
NuMA is present in the nucleolus of mammary epithelial cells. (A) Immunoblots for NuMA, ribosome-associated proteins fibrillarin and RPL26, cytoplasmic marker α-Tubulin and nucleoplasmic 53BP1 in total protein extracts (Total) and purified nucleoli fraction (Nucleoli) of T4–2 cells. (B). Electron micrographs of growth-arrested S1 cells (day 10) incubated with non-specific immunoglobulins (control) or with NuMA antibodies (NuMA) revealing the localization of NuMA (some of the gold particles [black dots] are indicated by arrows in the inset). A drawing illustrates the different nucleolar subcompartments. (C) Quantification of the distribution of NuMA gold immunolabeling particles within the FC and DFC/GC regions of the nucleoli as determined by the number of NuMA gold particles measured per area of FC and DFC/GC regions from the electron micrographs. The error bars on the scattered plot represent standard deviation. A total of eight nucleoli [areas ranging from ∼0.15 to 1 μm2] were analyzed with four nuclei containing one nucleolus per nucleus, three nuclei containing two nucleoli per nucleus and one nucleus containing three nucleoli; FC, fibrillar center; DFC, dense fibrillar center; GC, granular center.