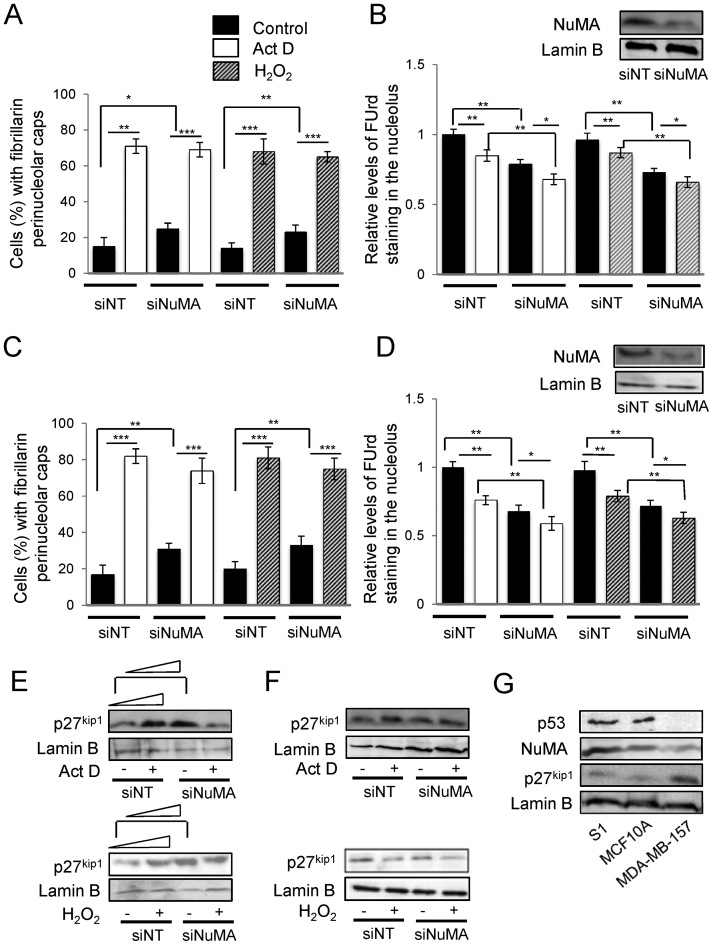
Figure 6.
Silencing NuMA and treatments with actinomycin D and H2O2 lead to p27kip1 increase unless it is already elevated. MCF10A WT-p53 cells and p53-null MDA-MB-157 cells were treated with either siRNA against NuMA (siNuMA) or non-targeting siRNA (siNT) and left in culture for 10 (MCF10A) or eight (MDA-MB-157) days, and/or with 0.08 μg/ml actinomycin D (Act D) or control DMSO for 4 h on day 10 (or 8), and/or with 250 μM of H2O2 for 4 h on day 10 (or 8). (A and C). Percentage of cells with perinucleolar caps of fibrillarin indicative of nucleolar stress (n = 3; 150 nuclei analyzed per condition) in MCF10A (A) and MDA-MB-157 (C) populations. (B and D). Levels of FUrd staining for nascent rRNA (nucleolus) following normalization to nucleoplasmic staining intensity (nascent mRNAs) under the different treatment conditions (n = 3; 100 nuclei analyzed per condition). Shown is a representative western blot of NuMA expression upon siNuMA treatment in MCF10A cells (B) and MDA-MB-157 cells (D). (E and F). Western blot and accompanying quantification (following standardization with lamin B and compared to the first band of each western blot) for p27kip1, following Act D or H2O2 treatment in the presence (siNuMA) or absence (siNT) of siRNA against NuMA; lamin B is used as loading control in MCF10A (E) and MDA-MB-157 (F) cells. (G). Western blot for p53, NuMA, p27kip1 and loading control lamin B in untreated S1, MCF10A and MDA-MB-157 cells.