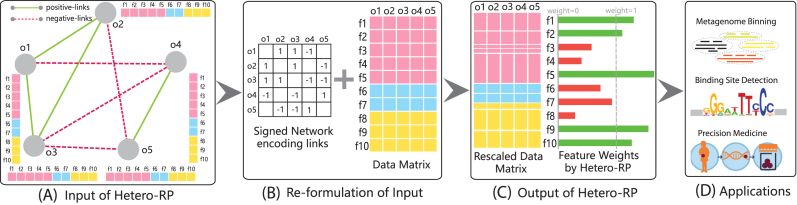
Figure 1.
Illustration of Hetero-RP on a toy example. (A) Each object o1, ⋅⋅⋅, o5 is represented by its corresponding feature vector, containing features indexed from f1 to f10, with colors indicating different data sources. ‘positive-links’ and ‘negative-links’ are in green solid line and red dash line, respectively. (B) The input to Hetero-RP contains two parts, the data matrix based on the concatenated feature vectors and the signed graph encoding both ‘positive-links’ and ‘negative-links’. (C) Hetero-RP rescales each dimension of features, but keeps the overall scale fixed. (D) The applications of Hetero-RP widely cover both clustering and classification domains.