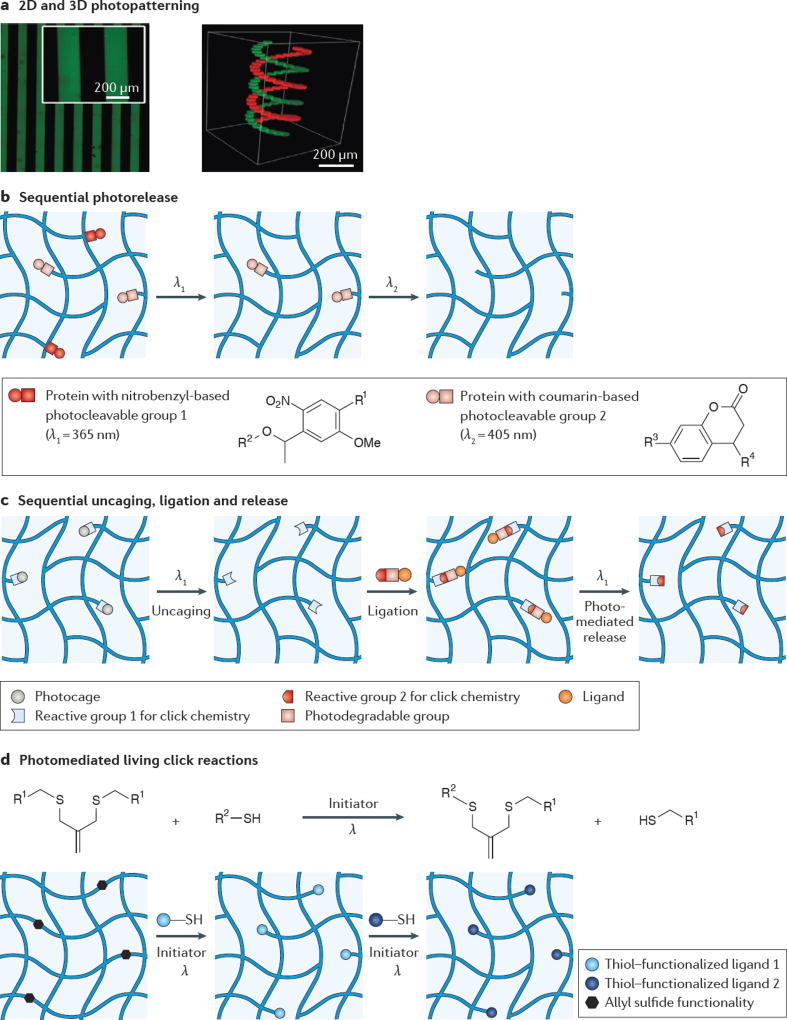
Figure 3. Light-based strategies for exchangeable ligand presentation.
a | Traditional lithographic masks are used for 2D photopatterning (left panel); however, 3D photopatterning (right panel) can access more complex shapes using a confocal laser scanning microscope. b | One strategy for the sequential release of biomolecules, such as proteins, relies on using photocleavable linkers with orthogonal absorption. For example, nitrobenzyl-based linkers cleave in response to 365 nm light and coumarin-based linkers cleave in response to 405 nm light. c | Another strategy for the reversible presentation of biomolecules first uncages a reactive group in the hydrogel, followed by ligation of the molecule (with a photocleavable linker) using click chemistry. The molecule can subsequently be removed using light, which cleaves the photodegradable linker. d | Living radical reactions, such as those mediated with an allyl sulfide functionality, provide opportunities for the reversible conjugation of biomolecules over many cycles. Panel a adapted with permission from REF. 48, Wiley-VCH. Panel b adapted with permission from REF 50, Wiley-VCH. Panel c from REF 49, Nature Publishing Group. Panel d adapted with permission from REF 54, Wiley-VCH.