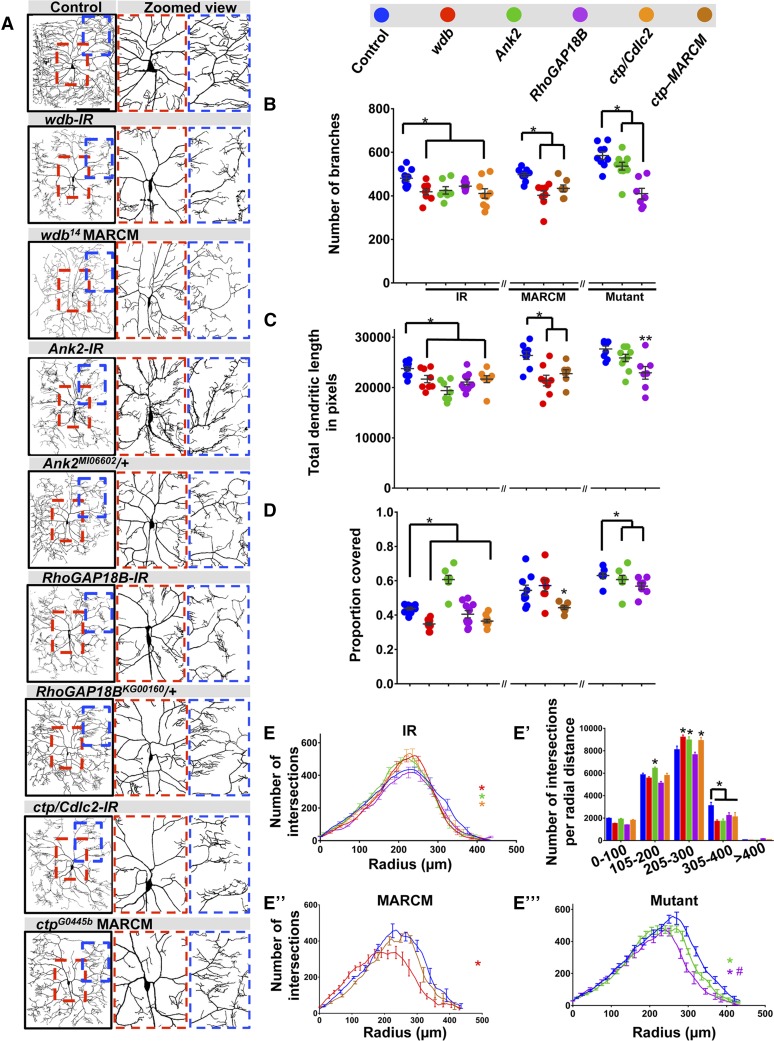
Figure 3.
Phenotypic analyses of Ct and Kn neurogenomic targets: Complexity shifter category. (A) Representative images of dendritic arborization in control, gene-specific RNAi knockdowns of CIV (ddaC) neurons (IR), MARCM clones, or heterozygous mutant alleles. (B and C) Quantitative analyses measuring number of branches (B) and total dendritic length (C), for RNAi knockdown (IR), MARCM and mutant analyses. (D) Quantification of the proportion of 10 × 10 pixel squares covered by dendrite in a 400 × 400 pixel region defined around the cell body. (E, E”, and E’’’) Sholl analysis profiles where values are the mean (± SEM) for the number of intersections as a function of radius distance (Euclidean) from the cell body (zero), where * and # refer to the significance scores for the critical value and the corresponding radius, respectively. (E’) Sholl profiles for IR data plotted as histogram to reflect the total number of intersections per corresponding radial distance (Euclidean) from the soma highlighting local effects on branch distributions. Statistical tests performed in: (B–E”’) one-way ANOVA with FDR correction of Benjamini, Kriega, and Yekutieli. N = 7–10 neurons, and significance scores were: * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, # P < 0.05. Bar, 200 µm.