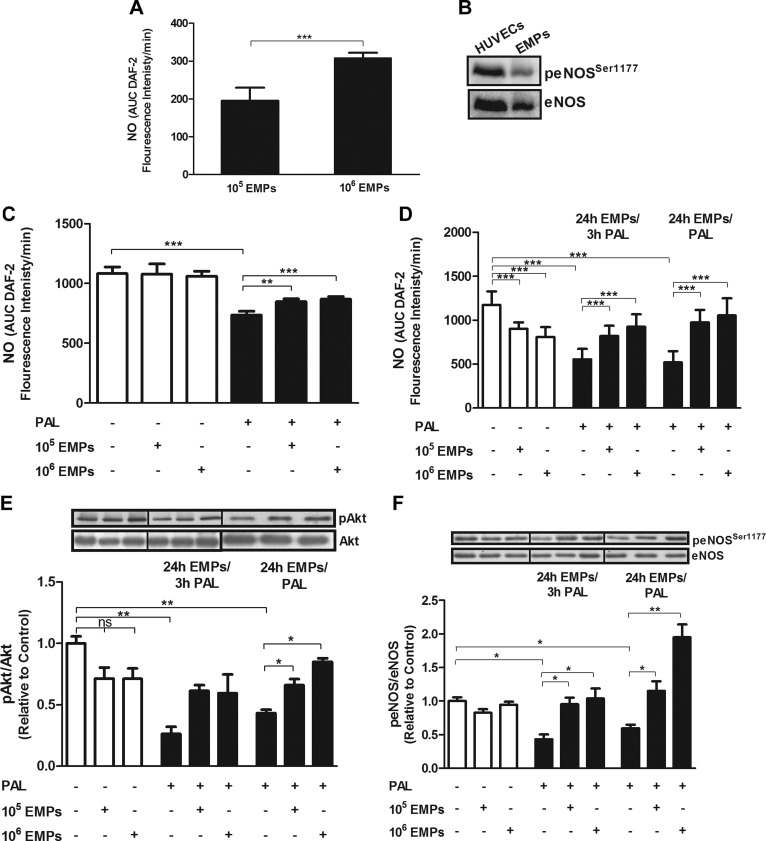
Figure 1.
EMPs express a functional eNOS, elevate NO in palmitate (Pal)-induced HUVECs, and increase phosphorylation levels of Akt and eNOS. A) EMPs were incubated with l-arginine for 5 min at 37°C, followed by the addition of DAF-2, and NO production was determined. EMPs produce eNOS-derived NO in a concentration-dependent manner, which is inhibited by the NOS inhibitor, L-NAME. The difference between fluorescence signal with and without L-NAME is considered NO production. B) peNOSSer1177 expression in EMPs and HUVECs as controls. C) HUVECs that were incubated with EMPs for 3 h showed no changes in NO production, whereas EMPs prevented the Pal-induced decline in NO production. D) Pal and EMPs diminish NO production. Treatment with either EMPs for 24 h with the addition of Pal during the last 3 h (24 h EMPs/3 h Pal) or with EMPs and Pal for 24 h (24 h EMPs/Pal) protects against Pal-induced reduction in NO production. Results are means ± sem; n = 8–12. E, F) Treatment of HUVECs with 100 µM Pal for either 3 or 24 h decreases protein phosphorylation of Akt (E) and eNOS at Ser1177 (F). EMPs up-regulate Akt and eNOS phosphorylation in HUVECs that are treated with either EMPs for 24 h with the addition of Pal during the last 3 h (24 h EMPs/3 h Pal) or with EMPs and Pal for 24 h (24 h EMPs/Pal). Results are means ± sem; n = 6 and analyzed using 1-way ANOVA. AUC, area under curve; ns, nonsignificant. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.