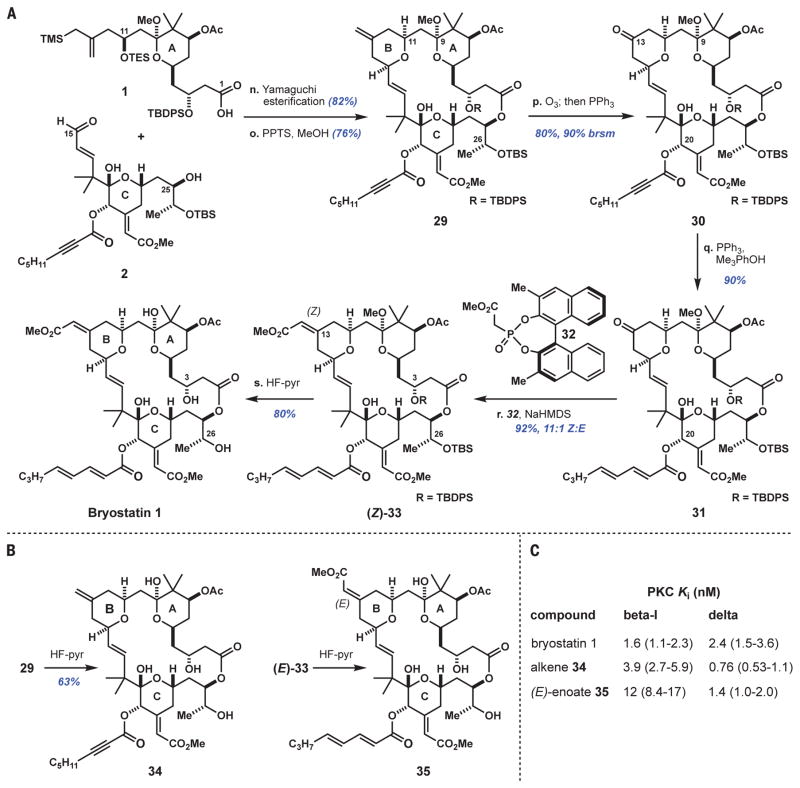
Fig. 4. Completion of bryostatin 1 synthesis and one-step diversifications toward analog compounds.
(A) Reaction sequence for bryostatin 1; (B) synthesis of derivatives 34 and 35; (C) characteristics of 34 and 35 versus bryostatin 1. Reagents and conditions: n. Acid 1 (1 equiv), 2,4,6-trichlorobenzoyl chloride (1.8 equiv), Et3N (6 equiv), toluene; then alcohol 2 (1 equiv), DMAP (3 equiv). o. PPTS (30 mol %), 50:1 MeOH/CH(OMe)3. p. Ozone (~1.9 equiv), MeOH/CH2Cl2, −78°C; then triphenylphosphine (Ph3P) (2 equiv), −78°C to room temperature. q. Ph3P (5 equiv), 2,4,6-trimethylphenol (5 equiv), benzene. r. Phosphonate 32 (14 equiv), sodium hexamethyldisilazide (NaHMDS) (13 equiv), THF, −78° to 4°C. s. 1:2:2 HF-pyridine/pyridine/THF, 40°C; then H2O, 40°C. See supplementary materials for PKC binding assay protocol. Error ranges in parentheses indicate 95% confidence intervals from nonlinear regression analysis.