Fig. 5.
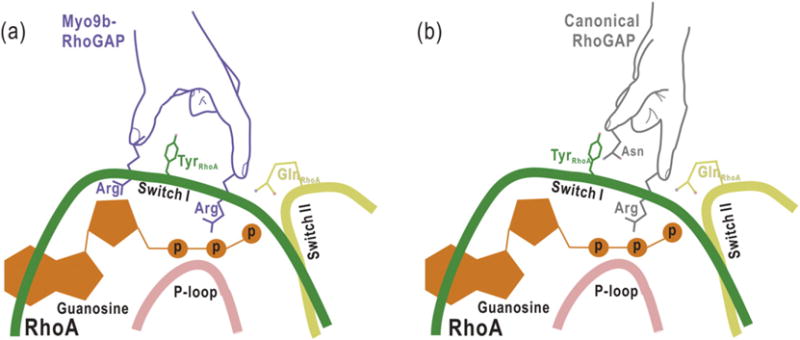
The proposed schematic models illustrating the catalytic mechanisms for Myo9b-RhoGAP and the canonical RhoGAP domain. Myo9b-RhoGAP contains two arginine fingers at the catalytic site (a), whereas the canonical RhoGAP domain has only one arginine finger together with an auxiliary asparagine (b). Similar to the catalytic arginine finger in canonical RhoGAP domain, the first arginine finger of Myo9b-RhoGAP inserts into the nucleotide-binding pocket of RhoA and interacts with the nucleotide for catalysis. In contrast, the second arginine finger of Myo9b-RhoGAP interacts with and stabilizes both the Switch I loop of RhoA and the nucleotide, which may compensate for the lack of the auxiliary asparagine residue in Myo9b-RhoGAP. Notably, a tyrosine residue from the Switch I loop of RhoA is sandwiched between the two arginine fingers of Myo9b-RhoGAP, further stabilizing the transition state of GTP hydrolysis.
